Frequency of RPE65 Gene Mutation in Patients with Hereditary Retinal Dystrophy
- PMID: 36017377
- PMCID: PMC9421938
- DOI: 10.4274/tjo.galenos.2021.74944
Frequency of RPE65 Gene Mutation in Patients with Hereditary Retinal Dystrophy
Abstract
Objectives: Hereditary retinal dystrophies are a rare group of diseases which are heterogeneous in genotype and phenotype and result in total blindness. One of the genetic defects that cause hereditary retinal dystrophy is mutation of the RPE65 gene. Genetic therapy studies in hereditary retinal dystrophies have increased in number recently, and important developments have been reported in these studies. Voretigene neparvovec-rzyl (Luxturna, Spark Therapeutics), a gene therapy drug for retinal dystrophy associated with RPE65 mutation, received Food and Drug Administration approval in 2017. This study aimed to investigate the frequency and clinical findings of patients with RPE65 gene defects, which may be amenable to genetic treatment.
Materials and methods: The data of patients diagnosed with hereditary retinal dystrophy who were followed up between 2017 and 2021 were retrospectively reviewed. Of these, 460 patients with genetic analysis results were included in the study. The clinical findings of patients with homozygous (biallelic) RPE65 mutation were screened.
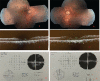
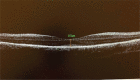
Results: RPE65 homozygous gene mutation was detected in only 11 of 460 cases (2.39%). Genetic results of the cases were presented in detail. The inheritance patterns of the cases were autosomal recessive. The demographic data and clinical findings were defined.
Conclusion: RPE65 gene mutation is a very rare disorder. Genetic screening has gained importance with the emergence of gene therapy alternatives. New treatment methods are promising in cases for which there was no chance of a cure to date.
Keywords: RPE65 gene; gene therapy; hereditary retinal dystrophy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Voretigene Neparvovec: A Review in RPE65 Mutation-Associated Inherited Retinal Dystrophy.Mol Diagn Ther. 2020 Aug;24(4):487-495. doi: 10.1007/s40291-020-00475-6. Mol Diagn Ther. 2020. PMID: 32535767 Review.
-
[Gene therapy treatment based on an ophthalmic indication in hereditary retinal dystrophy caused by RPE65 biallelic gene mutation.].Orv Hetil. 2022 Nov 27;163(48):1923-1931. doi: 10.1556/650.2022.32636. Print 2022 Nov 27. Orv Hetil. 2022. PMID: 36436058 Hungarian.
-
Clinical Perspective: Treating RPE65-Associated Retinal Dystrophy.Mol Ther. 2021 Feb 3;29(2):442-463. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.11.029. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Mol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33278565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of voretigene neparvovec (AAV2-hRPE65v2) in patients with RPE65-mediated inherited retinal dystrophy: a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial.Lancet. 2017 Aug 26;390(10097):849-860. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31868-8. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 28712537 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Inherited retinal dystrophy: first results of RPE65 gene replacement therapy in Russia].Vestn Oftalmol. 2022;138(4):48-57. doi: 10.17116/oftalma202213804148. Vestn Oftalmol. 2022. PMID: 36004591 Russian.
Cited by
-
Genetics and phenotypes of RPE65 mutations in inherited retinal degeneration: A study from a tertiary eye care center in Brazil.Mol Vis. 2025 Mar 16;31:45-54. eCollection 2025. Mol Vis. 2025. PMID: 40384766 Free PMC article.
-
Adeno-associated virus vectors for retinal gene therapy in basic research and clinical studies.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 1;10:1310050. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1310050. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38105897 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lorenz B, Gyürüs P, Preising M, Bremser D, Gu S, Andrassi M, Gerth C, Gal A. Early-onset severe rodcone dystrophy in young children with RPE65 mutations. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41:2735–2742. - PubMed
-
- Sevik MO, Şahin Ö. Leber Konjenital Amorozisi. Güncel Retina. 2021;5:173–184.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
