C-H Activation of Inert Arenes using a Photochemically Activated Guanidinato-Magnesium(I) Compound
- PMID: 36017712
- PMCID: PMC9828268
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.202202103
C-H Activation of Inert Arenes using a Photochemically Activated Guanidinato-Magnesium(I) Compound
Abstract
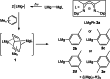
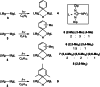
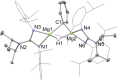
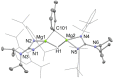
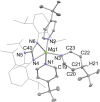
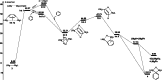
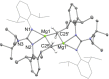
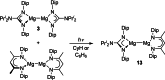
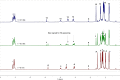
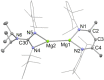
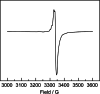
UV irradiation of solutions of a guanidinate coordinated dimagnesium(I) compound, [{(Priso)Mg}2 ] 3 (Priso=[(DipN)2 CNPri 2 ]- , Dip=2,6-diisopropylphenyl), in either benzene, toluene, the three isomers of xylene, or mesitylene, leads to facile activation of an aromatic C-H bond of the solvent in all cases, and formation of aryl/hydride bridged magnesium(II) products, [{(Priso)Mg}2 (μ-H)(μ-Ar)] 4-9. In contrast to similar reactions reported for β-diketiminate coordinated counterparts of 3, these C-H activations proceed with little regioselectivity, though they are considerably faster. Reaction of 3 with an excess of the pyridine, p-NC5 H4 But (pyBut ), gave [(Priso)Mg(pyBut H)(pyBut )2 ] 10, presumably via reduction of the pyridine to yield a radical intermediate, [(Priso)Mg(pyBut ⋅)(pyBut )2 ] 11, which then abstracts a proton from the reaction solvent or a reactant. DFT calculations suggest two possible pathways to the observed arene C-H activations. One of these involves photochemical cleavage of the Mg-Mg bond of 3, generating magnesium(I) doublet radicals, (Priso)Mg⋅. These then doubly reduce the arene substrate to give "Birch-like" products, which subsequently rearrange via C-H activation of the arene. Circumstantial evidence for the photochemical generation of transient magnesium radical species includes the fact that irradiation of a cyclohexane solution of 3 leads to an intramolecular aliphatic C-H activation process and formation of an alkyl-bridged magnesium(II) species, [{Mg(μ-Priso-H )}2 ] 12. Furthermore, irradiation of a 1 : 1 mixture of 3 and the β-diketiminato dimagnesium(I) compound, [{(Dip Nacnac)Mg}2 ] (Dip Nacnac=[HC(MeCNDip)2 ]- ), effects a "scrambling" reaction, and the near quantitative formation of an unsymmetrical dimagnesium(I) compound, [(Priso)Mg-Mg(Dip Nacnac)] 13. Finally, the EPR spectrum (77 K) of a glassed solution of UV irradiated 3 is dominated by a broad featureless signal, indicating the presence of a doublet radical species.
Keywords: C−H activation; low oxidation state; magnesium(I); photochemical; radical.
© 2022 The Authors. Chemistry - A European Journal published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
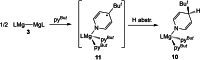
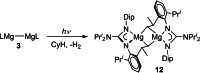
Similar articles
-
Photochemically Activated Dimagnesium(I) Compounds: Reagents for the Reduction and Selective C-H Bond Activation of Inert Arenes.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Mar 22;60(13):7087-7092. doi: 10.1002/anie.202017126. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 33474826
-
Molybdenum carbonyl assisted reductive tetramerization of CO by activated magnesium(i) compounds: squarate dianion vs. metallo-ketene formation.Chem Sci. 2023 Apr 24;14(19):5188-5195. doi: 10.1039/d3sc01487h. eCollection 2023 May 17. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 37206401 Free PMC article.
-
Reductive Metallation of Dendralenes and Myrcene Using Dimagnesium(I) Compounds: A Facile Route to Unsaturated Organomagnesium Compounds.Chemistry. 2024 Jan 26;30(6):e202303219. doi: 10.1002/chem.202303219. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Chemistry. 2024. PMID: 37985926
-
Bulky guanidinato nickel(I) complexes: synthesis, characterization, isomerization, and reactivity studies.Chemistry. 2011 Jan 24;17(4):1294-303. doi: 10.1002/chem.201002388. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Chemistry. 2011. PMID: 21243697
-
Calcium-Catalyzed Arene C-H Bond Activation by Low-Valent AlI.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Oct 21;58(43):15496-15503. doi: 10.1002/anie.201908978. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31465144 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assembly of Functionalized Organic Fragments via Reductive Activation and (Cross)-Coupling of C2H4, CO, CO2 and/or H2 Using a Magnesium-Dinitrogen Complex.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 May;64(19):e202500264. doi: 10.1002/anie.202500264. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 40016175 Free PMC article.
-
[{SiNDipp}MgNa]2: A Potent Molecular Reducing Agent.Organometallics. 2024 Apr 9;43(8):879-888. doi: 10.1021/acs.organomet.4c00076. eCollection 2024 Apr 22. Organometallics. 2024. PMID: 38665773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- See, for example:
-
- Labinger J. A., Bercaw J. E., Nature 2002, 417, 507–514; - PubMed
-
- Wencel-Delord J., Glorius F., Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 369–375; - PubMed
-
- Roudesly F., Oble J., Poli G., J. Mol. Catal. A 2017, 426, 275–296;
-
- Mkhalid I. A. I., Barnard J. H., Marder T. B., Murphy J. M., Hartwig J. F., Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 890–931; - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

