The burden of epilepsy and unmet need in people with focal seizures
- PMID: 36017757
- PMCID: PMC9480957
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.2589
The burden of epilepsy and unmet need in people with focal seizures
Abstract
Background: Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological conditions worldwide. As a chronic condition, epilepsy imposes a significant burden on people with epilepsy and society. We aimed to assess the burden and unmet need of individuals with epilepsy and their caregivers, focusing on focal seizures, the main type of seizure in adults and children.
Methods: A targeted evidence review of the burden of epilepsy, focusing on focal seizures, was conducted to identify articles reporting: epidemiology, mortality, morbidity, quality of life (QoL), and costs.
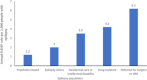
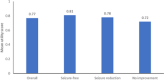
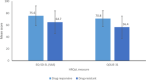
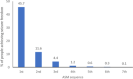
Results: Focal seizures affect up to ∼61% of people with epilepsy. They are associated with an increased risk of injury and premature death than the general population. People with epilepsy also have high comorbidity, particularly depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairments. Higher seizure frequency, adverse treatment events, and employment concerns reduce QoL. A reduction in caregivers' QoL is also often reported. Epilepsy requires long-term treatment accounting for high individual costs. Hospitalizations and antiseizure medications (ASMs) are the leading cost drivers of inpatient management and indirect costs with high unemployment rates, particularly in drug-resistant populations. Despite the advent of new treatments, a high unmet need remains unaddressed; approximately 40% of people with epilepsy are drug-resistant, further increasing the risks associated with epilepsy.
Conclusions: Our findings highlight a substantial burden of illness and unmet needs in individuals with focal seizures, especially those with drug-resistant epilepsy. Suboptimal treatment options negatively impact QoL and, consequently, a sizeable economic burden indicating the need for new treatments and prioritizing this condition.
Keywords: antiseizure medication; caregivers; costs; drug-resistant epilepsy; quality of life.
© 2022 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
SK Pharmaceuticals is the licensor of cenobamate. Persefoni Ioannou and Daniella L. Foster are full‐time employees at PHMR. PHMR received financial support from Arvelle Therapeutics for the work, including developing the review and drafting of the manuscript. Elena Alvarez‐Baron, Ewa Drogon O'Flaherty, and Jasmina Medjedovic are full‐time employees of Arvelle Therapeutics. Josemir W. Sander reports fees as speaker or consultant from Eisai, UCB, GW Pharma, Arvelle, and Zogenix. Other authors report no conflicts of interest concerning this work.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson, E. , Berkovic, S. , Dulac, O. , Gardiner, M. , Jain, S. , Friis, M. L. , Lindhout, D. , Noebels, J. , Ottman, R. , Scaramelli, A. , Serratosa, J. , Steinlein, O. , Avanzini, G. , Bailey‐Wilson, J. , Cardon, L. , Fischbach, R. , Gwinn‐Hardy, K. , Leppert, M. , Ott, J. , … Weiss, K. , & ILAE Genetics Commission . (2002). ILAE genetics commission conference report: Molecular analysis of complex genetic epilepsies. Epilepsia, 10, 1262–1267. - PubMed
-
- Aydemir, N. , Özkara, Ç. , Ünsal, P. , & Canbeyli, R. (2011). A comparative study of health related quality of life, psychological well‐being, impact of illness and stigma in epilepsy and migraine. Seizure: The Journal of the British Epilepsy Association, 20(9), 679–685. 10.1016/j.seizure.2011.06.017 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

