Role of the histone methyltransferases Ezh2 and Suv4-20h1/Suv4-20h2 in neurogenesis
- PMID: 36018148
- PMCID: PMC9727419
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.350188
Role of the histone methyltransferases Ezh2 and Suv4-20h1/Suv4-20h2 in neurogenesis
Abstract
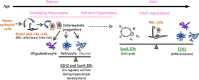
Mechanisms regulating neurogenesis involve broad and complex processes that represent intriguing therapeutic targets in the field of regenerative medicine. One influential factor guiding neural stem cell proliferation and cellular differentiation during neurogenesis are epigenetic mechanisms. We present an overview of epigenetic mechanisms including chromatin structure and histone modifications; and discuss novel roles of two histone modifiers, Ezh2 and Suv4-20h1/Suv4-20h2 (collectively referred to as Suv4-20h), in neurodevelopment and neurogenesis. This review will focus on broadly reviewing epigenetic regulatory components, the roles of epigenetic components during neurogenesis, and potential applications in regenerative medicine.
Keywords: Ezh2; Suv4-20h; adult neurogenesis; epigenetic; histone co-regulation; histone modification; neurodevelopment; neurogenesis; regenerative medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Lim DA. For the long run:maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron. 2004;41:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O. Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med. 2002;8:963–970. - PubMed
-
- Baker M. Making sense of chromatin states. Nat Methods. 2011;8:717–722. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

