Exosomal miR-23b from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviates oxidative stress and pyroptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage
- PMID: 36018178
- PMCID: PMC9727431
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.346551
Exosomal miR-23b from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviates oxidative stress and pyroptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage
Abstract
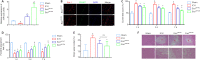
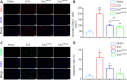
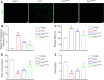
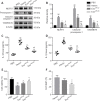
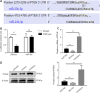
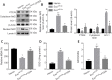
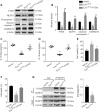
Our previous studies showed that miR-23b was downregulated in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). This indicates that miR-23b may be closely related to the patho-physiological mechanism of ICH, but this hypothesis lacks direct evidence. In this study, we established rat models of ICH by injecting collagenase VII into the right basal ganglia and treating them with an injection of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC)-derived exosomal miR-23b via the tail vein. We found that edema in the rat brain was markedly reduced and rat behaviors were improved after BMSC exosomal miR-23b injection compared with those in the ICH groups. Additionally, exosomal miR-23b was transported to the microglia/macrophages, thereby reducing oxidative stress and pyroptosis after ICH. We also used hemin to mimic ICH conditions in vitro. We found that phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) was the downstream target gene of miR-23b, and exosomal miR-23b exhibited antioxidant effects by regulating the PTEN/Nrf2 pathway. Moreover, miR-23b reduced PTEN binding to NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) and NLRP3 inflammasome activation, thereby decreasing the NLRP3-dependent pyroptosis level. These findings suggest that BMSC-derived exosomal miR-23b exhibits antioxidant effects through inhibiting PTEN and alleviating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis, thereby promoting neurologic function recovery in rats with ICH.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; Nrf2; PTEN; bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; exosomal miRNAs; intracerebral hemorrhage; miR-23b; neuroinflammation; oxidative stress; pyroptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures



Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviate neuroinflammation after diabetic intracerebral hemorrhage via the miR-183-5p/PDCD4/NLRP3 pathway.J Endocrinol Invest. 2021 Dec;44(12):2685-2698. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01583-8. Epub 2021 May 23. J Endocrinol Invest. 2021. PMID: 34024028
-
MicroRNA-23b alleviates neuroinflammation and brain injury in intracerebral hemorrhage by targeting inositol polyphosphate multikinase.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Nov;76:105887. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105887. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31536904
-
Exosomal miR-23b-3p from bone mesenchymal stem cells alleviates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting microglial pyroptosis.Exp Neurol. 2023 May;363:114374. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114374. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Exp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36907352
-
Neuroinflammation Mediated by NLRP3 Inflammasome After Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Potential Therapeutic Targets.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Dec;57(12):5130-5149. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02082-2. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32856203 Review.
-
Perspectives on the mechanism of pyroptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 5;13:989503. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.989503. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36131917 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Mechanism of Astragaloside IV in NOD-like Receptor Family Pyrin Domain Containing 3 Inflammasome-mediated Pyroptosis after Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2024;21(1):74-85. doi: 10.2174/0115672026295640240212095049. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 38409729
-
Insight into extracellular vesicles in vascular diseases: intercellular communication role and clinical application potential.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Oct 31;21(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01304-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37907962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of stem cell-derived exosomes in regulating pyroptosis for disease therapy.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jul 18;16(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04519-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40682142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signature and function of plasma exosome-derived circular RNAs in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage.Mol Genet Genomics. 2024 May 11;299(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s00438-024-02144-3. Mol Genet Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38734849
-
Natural and engineered extracellular vesicles in vascular diseases: a focus on therapeutic effects, challenges and prospective.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 1;30(1):524. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02822-x. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40597441 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bushati N, Cohen SM. microRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:175–205. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Guo C, Huang S, Jia Z, Wang J, Zhong J, Ge H, Yuan J, Chen T, Liu X, Hu R, Yin Y, Feng H. MitoQ attenuates brain damage by polarizing microglia towards the M2 phenotype through inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome after ICH. Pharmacol Res. 2020b;161:105122. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Zhou Y, Wang S, Wang W. Mechanism of baicalein in brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage by inhibiting the ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Inflammation. 2022;45:590–602. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

