Standard-Free Absolute Quantitation of Antibody Deamidation Degradation and Host Cell Proteins by Coulometric Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 36018377
- PMCID: PMC10492508
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c02709
Standard-Free Absolute Quantitation of Antibody Deamidation Degradation and Host Cell Proteins by Coulometric Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
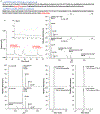
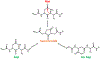
Proteomic absolute quantitation strategies mainly rely on the use of synthetic stable isotope-labeled peptides or proteins as internal standards, which are highly costly and time-consuming to synthesize. To circumvent this limitation, we recently developed a coulometric mass spectrometry (CMS) approach for absolute quantitation of proteins without the use of standards, based on the electrochemical oxidation of oxidizable surrogate peptides, followed by mass spectrometry measurement of the peptide oxidation yield. Previously, CMS was only applied for single-protein quantitation. In this study, first, we demonstrated absolute quantitation of multiple proteins in a mixture (e.g., β-lactoglobulin B, α-lactalbumin, and carbonic anhydrase) by CMS in one run, without using any standards. The CMS quantitation result was validated with a traditional isotope dilution method. Second, CMS can be used for absolute quantitation of a low-level target protein in a mixture; for instance, 500 ppm of PLBL2, a problematic host cell protein (HCP), in the presence of a highly abundant monoclonal antibody (mAb) was successfully quantified by CMS with no use of standards. Third, taking one step further, this study demonstrated the unprecedented quantitative analysis of deamidated peptide products arising from the mAb heavy chain deamidation reaction. In particular, absolute quantitation of the deamidation succinimide intermediate which had not been performed before due to the lack of standard was conducted by CMS, for the first time. Overall, our data suggest that CMS has potential utilities for quantitative proteomics and biotherapeutic drug discovery.
Figures


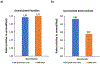
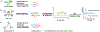
Similar articles
-
Absolute Quantitation of Tryptophan-Containing Peptides and Amyloid β-Peptide Fragments by Coulometric Mass Spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021 Jul 7;32(7):1771-1779. doi: 10.1021/jasms.1c00121. Epub 2021 Jun 8. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021. PMID: 34101439 Free PMC article.
-
Standards-Free Absolute Quantitation of Oxidizable Glycopeptides by Coulometric Mass Spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2024 Jul 3;35(7):1441-1450. doi: 10.1021/jasms.4c00052. Epub 2024 May 30. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2024. PMID: 38815255
-
Absolute Quantitation of Proteins by Coulometric Mass Spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2020 Jun 2;92(11):7877-7883. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01151. Epub 2020 May 15. Anal Chem. 2020. PMID: 32368902
-
Isotope dilution mass spectrometry for absolute quantification in proteomics: concepts and strategies.J Proteomics. 2014 Jan 16;96:184-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 11. J Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24231108 Review.
-
Methods and Algorithms for Quantitative Proteomics by Mass Spectrometry.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2051:161-197. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9744-2_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31552629 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of Vaccines Formulation to Tackle the Challenge of Anti-Microbial Resistant Pathogens.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 27;24(15):12054. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512054. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Absolute Quantitation of Peptides and Proteins by Coulometric Mass Spectrometry After Derivatization.Int J Mass Spectrom. 2024 Jan;495:117153. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2023.117153. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2024. PMID: 38009161 Free PMC article.
-
Stability of Protein Pharmaceuticals: Recent Advances.Pharm Res. 2024 Jul;41(7):1301-1367. doi: 10.1007/s11095-024-03726-x. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 38937372 Review.
References
-
- Pagala VR; High AA; Wang X; Tan H; Kodali K; Mishra A; Kavdia K; Xu Y; Wu Z; Peng J, Quantitative protein analysis by mass spectrometry. In Protein-Protein Interactions, Springer: 2015; pp 281–305. - PubMed
-
- Garcia BA, Quantitative proteomics for understanding modified proteins and proteomes. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 474.1–474.1.
-
- Gygi SP; Rist B; Gerber SA; Turecek F; Gelb MH; Aebersold R, Quantitative analysis of complex protein mixtures using isotope-coded affinity tags. Nat. Biotechnol 1999, 17 (10), 994–999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

