Full-length recombinant antibodies from Escherichia coli: production, characterization, effector function (Fc) engineering, and clinical evaluation
- PMID: 36018829
- PMCID: PMC9423848
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2022.2111748
Full-length recombinant antibodies from Escherichia coli: production, characterization, effector function (Fc) engineering, and clinical evaluation
Abstract
Although several antibody fragments and antibody fragment-fusion proteins produced in Escherichia coli (E. coli) are approved as therapeutics for various human diseases, a full-length monoclonal or a bispecific antibody produced in E. coli has not yet been approved. The past decade witnessed substantial progress in expression of full-length antibodies in the E. coli cytoplasm and periplasm, as well as in cell-free expression systems. The equivalency of E. coli-produced aglycosylated antibodies and their mammalian cell-produced counterparts, with respect to biochemical and biophysical properties, including antigen binding, in vitro and in vivo serum stability, pharmacokinetics, and in vivo serum half-life, has been demonstrated. Extensive engineering of the Fc domain of aglycosylated antibodies enables recruitment of various effector functions, despite the lack of N-linked glycans. This review summarizes recent research, preclinical advancements, and clinical development of E. coli-produced aglycosylated therapeutic antibodies as monoclonal, bispecific, and antibody-drug conjugates for use in autoimmune, oncology, and immuno-oncology areas.Abbreviations: ADA Anti-drug antibody; ADCC Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; ADCP Antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis; ADC Antibody-drug conjugate; aFc Aglycosylated Fc; AMD Age-related macular degeneration aTTP Acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; BCMA B-cell maturation antigen; BLA Biologics license application; BsAb Bispecific antibody; C1q Complement protein C1q; CDC Complement-dependent cytotoxicity; CDCC Complement-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; CDCP Complement-dependent cellular phagocytosis; CEX Cation exchange chromatography; CFPS Cell-free protein expression; CHO Chinese Hamster Ovary; CH1-3 Constant heavy chain 1-3; CL Constant light chain; DLBCL Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; DAR Drug antibody ratio; DC Dendritic cell; dsFv Disulfide-stabilized Fv; EU European Union; EGFR Epidermal growth factor receptor; E. coli Escherichia coli; EpCAM Epithelial cell adhesion molecule; Fab Fragment antigen binding; FACS Fluorescence activated cell sorting; Fc Fragment crystallizable; FcRn Neonatal Fc receptor; FcɣRs Fc gamma receptors; FDA Food and Drug Administration; FL-IgG Full-length immunoglobulin; Fv Fragment variable; FolRαa Folate receptor alpha; gFc Glycosylated Fc; GM-CSF Granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor; GPx7 Human peroxidase 7; HCL Hairy cell leukemia; HIV Human immunodeficiency virusl; HER2 Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; HGF Hepatocyte growth factor; HIC Hydrophobic interaction chromatography; HLA Human leukocyte antigen; IBs Inclusion bodies; IgG1-4 Immunoglobulin 1-4; IP Intraperitoneal; ITC Isothermal titration calorimetry; ITP Immune thrombocytopenia; IV Intravenous; kDa Kilodalton; KiH Knob-into-Hole; mAb Monoclonal antibody; MAC Membrane-attack complex; mCRC Metastatic colorectal cancer; MM Multipl myeloma; MOA Mechanism of action; MS Mass spectrometry; MUC1 Mucin 1; MG Myasthenia gravis; NB Nanobody; NK Natural killer; nsAA Nonstandard amino acid; NSCLC Non-small cell lung cancer; P. aeruginosa Pseudomonas aeruginosa; PD-1 Programmed cell death 1; PD-L1 Programmed cell death-ligand 1; PDI Protein disulfide isomerase; PECS Periplasmic expression cytometric screening; PK Pharmacokinetics; P. pastoris Pichia pastoris; PTM Post-translational modification; Rg Radius of gyration; RA Rheumatoid arthritis; RT-PCR Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; SAXS Small angle X-ray scattering; scF Single chain Fv; SCLC Small cell lung cancer; SDS-PAGE Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; SEC Size exclusion chromatography; SEED Strand-exchange engineered domain; sRNA Small regulatory RNA; SRP Signal recognition particle; T1/2 Half-life; Tagg Aggregation temperature; TCR T cell receptor; TDB T cell-dependent bispecific; TF Tissue factor; TIR Translation initiation region; Tm Melting temperature; TNBC Triple-negative breast cancer; TNF Tumor necrosis factor; TPO Thrombopoietin; VEGF Vascular endothelial growth factor; vH Variable heavy chain; vL Variable light chain; vWF von Willebrand factor; WT Wild type.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; Fc engineering; aglycosylated antibody; bispecific antibody; cell-free expression; disulfide bond; effector function; full-length immunoglobulin; monoclonal antibody; semi-oxidizing cytoplasm.
Conflict of interest statement
The author reports no conflicts of interest. The author alone is responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Figures
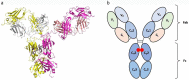
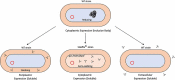
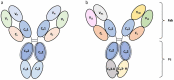
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
