Social capital as a network measure provides new insights on economic growth
- PMID: 36018843
- PMCID: PMC9417001
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273066
Social capital as a network measure provides new insights on economic growth
Abstract
Unveiling the main drivers of economic growth is of paramount importance. Previous research recognizes the critical role played by the factors of production: capital and labor. However, the exact mechanisms that underpin Total Factor Productivity (TFP) are not fully understood. An increasing number of studies suggests that the creation and transmission of knowledge, factor supply and economic integration are indeed crucial. Yet, the need for a systematic and unifying framework still exists. Nowadays capital and labor are embedded into a complex network structure through global supply chains and international migration. Recent research has established a link between network centralities and different types of social capital. In this work we employ the OECD's Multi-Regional Input-Output and International Migration datasets to build the network representation for capital and labor of 63 economies during 10 years. We then examine the role of social capital measures as drivers of the TFP adopting an extended Cobb-Douglass production function and addressing potential issues such as multicollinearity, reverse causality and non-linear effects. Our results indicate that social capital in the factors of production networks can significantly drive economic outputs through TFP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


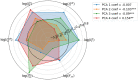

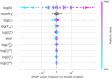
Similar articles
-
Assessing the total factor productivity growth decomposition: the transformation of economic growth momentum and policy choice in China.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Mar;30(12):34503-34517. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-24282-0. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36513901
-
Evaluating the carbon total factor productivity of China: based on Cobb-Douglas production function.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Feb;31(9):13722-13738. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32070-1. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38265585
-
The world economic system and international migration in less developed countries: an ecological approach.Int Migr. 1995;33(1):93-114. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2435.1995.tb00020.x. Int Migr. 1995. PMID: 12346351
-
[The role of the state in the migration of workers and economic diversification in the countries of the Arab Peninsula].Tiers Monde (1960). 1985 Jul-Sep;26(103):597-620. Tiers Monde (1960). 1985. PMID: 12280378 French.
-
Measures of equity for multi-capital accounting.Nat Food. 2021 Sep;2(9):646-654. doi: 10.1038/s43016-021-00336-3. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Nat Food. 2021. PMID: 37117461 Review.
Cited by
-
The contagion effect of heterogeneous investor groups.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 18;18(10):e0292795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292795. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37851630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Solow RM. Technical Change and the Aggregate Production Function. The Review of Economics and Statistics. 1957;39(3):312–320. doi: 10.2307/1926047 - DOI
-
- Ramsey FP. A Mathematical Theory of Saving. The Economic Journal. 1928;38(152):543–559. doi: 10.2307/2224098 - DOI
-
- Romer PM. Endogenous Technological Change. Journal of Political Economy. 1990;98(5, Part 2):S71–S102. doi: 10.1086/261725 - DOI
-
- Aghion P, Howitt P. A model of growth through creative destruction; 1990.
-
- Lucas RE. On the mechanics of economic development. Journal of Monetary Economics. 1988;22(1):3–42. doi: 10.1016/0304-3932(88)90168-7 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

