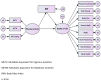
Structural model of the relationship between physical activity and students' quality of life: Mediating role of body mass index and moderating role of gender
- PMID: 36018894
- PMCID: PMC9416990
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273493
Structural model of the relationship between physical activity and students' quality of life: Mediating role of body mass index and moderating role of gender
Abstract
Background: As a country's future leaders and pioneers, University students must live with healthy habits. In order to achieve a healthy lifestyle, Physical activity and Quality of Life can serve as suitable indices to study. The purpose of the study was to clarify how physical activity (PA), Body mass index (BMI) and gender relate to the quality of life (QOL) of students of Medical Sciences University by using a structural equation model.
Methods: The research was a cross-sectional study. The number of participants was 225 students of the University. The participants answered three questionnaires, including Demographic, International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ short form), and Quality of Life Questionnaire (SF-12), BMI was calculated by anthropometric measures, as well. The Structural equation model (SEM) method was employed. The Fitness of the proposed pattern was measured using the following indexes: chi-square/degree of freedom ratio (CMIN/DF), Normed Fit Index (NFI), comparative fit index (CFI), the goodness of fit index (GFI), and standardized root mean squared residual (SRMR). In the analysis the significant level was considered as P < 0.05.
Results: PA (r = -0.726, P<0.001) and QOL (r = -0.405, P<0.001) have significantly inverse relationship with BMI, whereas the QOL and PA were proven to be positively related (r = 0.357, P<0.001). Moreover, the results signify gender as a moderator in the relationship between PA and QOL (Δχ2 (10) = 19.903, P = 0.030) and also the mediatory role of BMI among students. BMI affects the QOL in men (P < 0.001, β = -0.307) more in compare to women women (P = 0.324, β = -0.158).
Conclusion: Study findings supported the research hypothesis. Gender exhibited moderating role in the relationship between PA and QOL, considering the mediating role of BMI.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Personality traits and quality of life among Lebanese medical students: any mediating effect of emotional intelligence? A path analysis approach.BMC Psychol. 2022 Feb 11;10(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s40359-022-00739-2. BMC Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35148803 Free PMC article.
-
Path Analysis of Campus Walkability/Bikeability and College Students' Physical Activity Attitudes, Behaviors, and Body Mass Index.Am J Health Promot. 2018 Mar;32(3):578-586. doi: 10.1177/0890117116666357. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Am J Health Promot. 2018. PMID: 27630109
-
Structural equation model of affecting factors on elder abuse to patients under hemodialysis by family caregivers.BMC Geriatr. 2021 Jun 12;21(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02291-x. BMC Geriatr. 2021. PMID: 34118877 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Body Image, Disordered Eating and Lifestyle on the Quality of Life in Lithuanian University Students.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Mar 2;17(5):1593. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051593. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32121625 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity and quality of life among university students: exploring self-efficacy, self-esteem, and affect as potential mediators.Qual Life Res. 2014 Mar;23(2):659-67. doi: 10.1007/s11136-013-0492-8. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Qual Life Res. 2014. PMID: 23928820 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association Between Quality of Life and Body Mass Index Among First-Year Medical Students in a Peruvian Private University: A Single-Center Cross-Sectional Pilot Study.Cureus. 2025 Mar 28;17(3):e81378. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81378. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40291295 Free PMC article.
-
Physical self-perception as mediator between physical activity and quality of life among Chinese university students.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 7;15(1):24184. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08810-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40624274 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Activity, BMI, and Their Effects on University Students' Quality of Life.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Aug 1;13(15):1880. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13151880. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grujic S. Ucestalost i problemi kvantifikacije gojaznosti predskolske dece [The frequency and problems of quantification overweight and preschool children] Faculty of Sport and Tourism, Novi Sad. TIMS Acta. 2011; 5: 31–36. Serbian.
-
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (Accessed 30 May 2021).
-
- Organization WH. New physical activity recommendations for reducing disease and prevent deaths. 2011.
-
- Orsega-Smith EM, Payne LL, Mowen AJ, Ho C-H, Godbey GC. The role of social support and self-efficacy in shaping the leisure time physical activity of older adults. Journal of Leisure research. 2007;39(4):705–27.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous