Multiple BCG vaccinations for the prevention of COVID-19 and other infectious diseases in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 36027906
- PMCID: PMC9376308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100728
Multiple BCG vaccinations for the prevention of COVID-19 and other infectious diseases in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
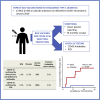
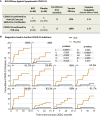
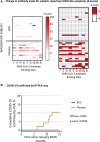
There is a need for safe and effective platform vaccines to protect against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and other infectious diseases. In this randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase 2/3 trial, we evaluate the safety and efficacy of a multi-dose Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19 and other infectious disease in a COVID-19-unvaccinated, at-risk-community-based cohort. The at-risk population is made of up of adults with type 1 diabetes. We enrolled 144 subjects and randomized 96 to BCG and 48 to placebo. There were no dropouts over the 15-month trial. A cumulative incidence of 12.5% of placebo-treated and 1% of BCG-treated participants meets criteria for confirmed COVID-19, yielding an efficacy of 92%. The BCG group also displayed fewer infectious disease symptoms and lesser severity and fewer infectious disease events per patient, including COVID-19. There were no BCG-related systemic adverse events. BCG's broad-based infection protection suggests that it may provide platform protection against new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants and other pathogens.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02081326.
Keywords: BCG; Bacillus Calmette-Guérin; COVID-19; Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT02081326; autoimmune; host microbe interactions; hygiene hypothesis; infectious diseases; phase 2/3 trial; randomized double blinded clinical trial; type 1 diabetes; vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests No author or author family member owns patents on this work. No author has any ownership rights to the study drug. No authors receive consulting or research support from Japan Laboratories.
Figures



References
-
- Anonymous BCG vaccines: WHO position paper. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2018
-
- Aaby P., Roth A., Ravn H., Napirna B.M., Rodrigues A., Lisse I.M., Stensballe L., Diness B.R., Lausch K.R., Lund N., et al. Randomized trial of BCG vaccination at birth to low-birth-weight children: beneficial nonspecific effects in the neonatal period? J. Infect. Dis. 2011;204:245–252. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir240. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Biering-Sorensen S., Aaby P., Lund N., Monteiro I., Jensen K.J., Eriksen H.B., Schaltz-Buchholzer F., Jorgensen A.S.P., Rodrigues A., Fisker A.B., Benn C.S. Early BCG-Denmark and neonatal mortality among infants weighing <2500 g: a randomized controlled trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017;65:1183–1190. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix525. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biering-Sorensen S., Aaby P., Napirna B.M., Roth A., Ravn H., Rodrigues A., Whittle H., Benn C.S. Small randomized trial among low-birth-weight children receiving bacillus Calmette-Guerin vaccination at first health center contact. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2012;31:306–308. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182458289. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

