Virus variant-specific clinical performance of SARS coronavirus two rapid antigen tests in point-of-care use, from November 2020 to January 2022
- PMID: 36028089
- PMCID: PMC9398563
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2022.08.006
Virus variant-specific clinical performance of SARS coronavirus two rapid antigen tests in point-of-care use, from November 2020 to January 2022
Abstract
Objectives: Antigen rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) for SARS coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) are quick, widely available, and inexpensive. Consequently, RDTs have been established as an alternative and additional diagnostic strategy to quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). However, reliable clinical and large-scale performance data specific to a SARS-CoV-2 virus variant of concern (VOC) are limited, especially for the Omicron VOC. The aim of this study was to compare RDT performance among different VOCs.
Methods: This single-centre prospective performance assessment compared RDTs from three manufacturers (NADAL, Panbio, MEDsan) with RT-qPCR including deduced standardized viral load from oropharyngeal swabs for detection of SARS-CoV-2 in a clinical point-of-care setting from November 2020 to January 2022.
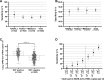
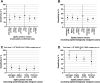
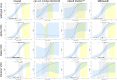
Results: Among 35 479 RDT/RT-qPCR tandems taken from 26 940 individuals, 164 of the 426 SARS-CoV-2 positive samples tested true positive with an RDT corresponding to an RDT sensitivity of 38.50% (95% CI, 34.00-43.20%), with an overall specificity of 99.67% (95% CI, 99.60-99.72%). RDT sensitivity depended on viral load, with decreasing sensitivity accompanied by descending viral load. VOC-dependent sensitivity assessment showed a sensitivity of 42.86% (95% CI, 32.82-53.52%) for the wild-type SARS-CoV-2, 43.42% (95% CI, 32.86-54.61%) for the Alpha VOC, 37.67% (95% CI, 30.22-45.75%) for the Delta VOC, and 33.67% (95% CI, 25.09-43.49%) for the Omicron VOC. Sensitivity in samples with high viral loads of ≥106 SARS-CoV-2 RNA copies per mL was significantly lower in the Omicron VOC (50.00%; 95% CI, 36.12-63.88%) than in the wild-type SARS-CoV-2 (79.31%; 95% CI, 61.61-90.15%; p 0.015).
Discussion: RDT sensitivity for detection of the Omicron VOC is reduced in individuals infected with a high viral load, which curtails the effectiveness of RDTs. This aspect furthert: limits the use of RDTs, although RDTs are still an irreplaceable diagnostic tool for rapid, economic point-of-care and extensive SARS-CoV-2 screening.
Keywords: Antigen rapid diagnostic test; Clinical performance evaluation; Omicron; PCR; SARS-CoV-2; Virus variants of concern.
Copyright © 2022 European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization Use of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detection rapid diagnostic tests for COVID-19 self-testing. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-Ag-RDTs-Self_testi... Available at:
-
- Barrera-Avalos C., Luraschi R., Vallejos-Vidal E., Mella-Torres A., Hernández F., Figueroa M., et al. The rapid antigen detection test for SARS-CoV-2 underestimates the identification of covid-19 positive cases and compromises the diagnosis of the SARS-CoV-2 (K417N/T, E484K, and N501Y) variants. Front Public Health. 2021;9 doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.780801. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bekliz M., Perez-Rodriguez F., Puhach O., Adea K., Melancia S.M., Baggio S., et al. Sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid tests for Omicron variant. medRxiv. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.18.21268018v2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

