Genome Protection by DNA Polymerase θ
- PMID: 36028228
- PMCID: PMC10351424
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-genet-072920-041046
Genome Protection by DNA Polymerase θ
Abstract
DNA polymerase θ (Pol θ) is a DNA repair enzyme widely conserved in animals and plants. Pol θ uses short DNA sequence homologies to initiate repair of double-strand breaks by theta-mediated end joining. The DNA polymerase domain of Pol θ is at the C terminus and is connected to an N-terminal DNA helicase-like domain by a central linker. Pol θ is crucial for maintenance of damaged genomes during development, protects DNA against extensive deletions, and limits loss of heterozygosity. The cost of using Pol θ for genome protection is that a few nucleotides are usually deleted or added at the repair site. Inactivation of Pol θ often enhances the sensitivity of cells to DNA strand-breaking chemicals and radiation. Since some homologous recombination-defective cancers depend on Pol θ for growth, inhibitors of Pol θ may be useful in treating such tumors.
Keywords: DNA double-strand breaks; DNA helicase; DNA polymerases; DNA repair; mutations; translesion DNA synthesis.
Figures
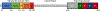
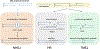
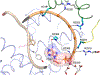

Similar articles
-
A non-tethering role for the Drosophila Pol θ linker domain in promoting damage resolution.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Apr 22;53(8):gkaf304. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf304. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40275613 Free PMC article.
-
DNA polymerase θ (POLQ), double-strand break repair, and cancer.DNA Repair (Amst). 2016 Aug;44:22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.05.003. Epub 2016 May 14. DNA Repair (Amst). 2016. PMID: 27264557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and Structural Analyses of Human DNA Polymerase θ (POLQ).Methods Enzymol. 2017;592:103-121. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2017.03.026. Epub 2017 May 24. Methods Enzymol. 2017. PMID: 28668117 Free PMC article.
-
RETRACTED: Human DNA polymerase θ harbors DNA end-trimming activity critical for DNA repair.Mol Cell. 2021 Apr 1;81(7):1534-1547.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.01.021. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Mol Cell. 2021. Retraction in: Mol Cell. 2024 Apr 18;84(8):1626. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.03.024. PMID: 33577776 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
DNA polymerase theta (Polθ) - an error-prone polymerase necessary for genome stability.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020 Feb;60:119-126. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2020.02.017. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020. PMID: 32302896 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the DNA damage response in cancer.MedComm (2020). 2024 Oct 31;5(11):e788. doi: 10.1002/mco2.788. eCollection 2024 Nov. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39492835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A non-tethering role for the Drosophila Pol θ linker domain in promoting damage resolution.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Apr 22;53(8):gkaf304. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf304. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40275613 Free PMC article.
-
The tardigrade Hypsibius exemplaris dramatically upregulates DNA repair pathway genes in response to ionizing radiation.Curr Biol. 2024 May 6;34(9):1819-1830.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.03.019. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Curr Biol. 2024. PMID: 38614079 Free PMC article.
-
A mobile genetic element-derived primase-polymerase harbors multiple activities implicated in DNA replication and repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 11;53(2):gkae1318. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1318. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39797730 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic interplay of cNHEJ and MMEJ pathways of DNA double-strand break repair during embryonic development in zebrafish.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 10;15(1):4886. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88564-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39929954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi N, So S, Koyama H. 2004. Loss of nonhomologous end joining confers camptothecin resistance in DT40 cells. Implications for the repair of topoisomerase I-mediated DNA damage. J. Biol. Chem 279:37343–48 - PubMed
-
- Aguirrezabalaga I, Sierra LM, Comendador MA. 1995. The hypermutability conferred by the mus308 mutation of Drosophila is not specific for cross-linking agents. Mutat. Res 336:243–50 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

