Ammonia promotes the proliferation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating the Akt/mTOR/S6k pathway
- PMID: 36028500
- PMCID: PMC9418171
- DOI: 10.1038/s41413-022-00215-y
Ammonia promotes the proliferation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating the Akt/mTOR/S6k pathway
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Ammonia promotes the proliferation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating the Akt/mTOR/S6k pathway.Bone Res. 2024 Feb 20;12(1):9. doi: 10.1038/s41413-024-00314-y. Bone Res. 2024. PMID: 38378665 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
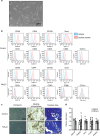
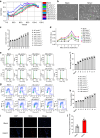
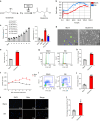
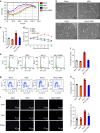
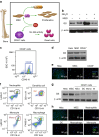
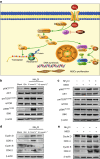
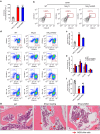
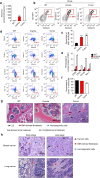
Ammonia plays an important role in cellular metabolism. However, ammonia is considered a toxic product. In bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells, multipotent stem cells with high expression of glutamine synthetase (GS) in bone marrow, ammonia and glutamate can be converted to glutamine via glutamine synthetase activity to support the proliferation of MSCs. As a major nutritional amino acid for biosynthesis, glutamine can activate the Akt/mTOR/S6k pathway to stimulate cell proliferation. The activation of mTOR can promote cell entry into S phase, thereby enhancing DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. Our studies demonstrated that mesenchymal stem cells can convert the toxic waste product ammonia into nutritional glutamine via GS activity. Then, the Akt/mTOR/S6k pathway is activated to promote bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell proliferation. These results suggest a new therapeutic strategy and potential target for the treatment of diseases involving hyperammonemia.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Author Correction: Ammonia promotes the proliferation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating the Akt/mTOR/S6k pathway.Bone Res. 2024 Feb 20;12(1):9. doi: 10.1038/s41413-024-00314-y. Bone Res. 2024. PMID: 38378665 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Peptide hormone ELABELA promotes rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and migration by manipulating the cell cycle through the PI3K/AKT pathway under the hypoxia and ischemia microenvironment.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jan 28;13(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02691-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35090551 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine synthetase in brain: effect of ammonia.Neurochem Int. 2002 Aug-Sep;41(2-3):123-42. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(02)00033-5. Neurochem Int. 2002. PMID: 12020613 Review.
-
The razor clam Sinonovacula constricta uses the strategy of conversion of toxic ammonia to glutamine in response to high environmental ammonia exposure.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Dec;47(12):9579-9593. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-06018-w. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33245503
-
Glutamine Metabolism Is Essential for Stemness of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Bone Homeostasis.Stem Cells Int. 2019 Sep 12;2019:8928934. doi: 10.1155/2019/8928934. eCollection 2019. Stem Cells Int. 2019. PMID: 31611919 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Photobiomodulation promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and increases P-Akt levels in vitro.Sci Rep. 2025 May 22;15(1):17844. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02428-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40404710 Free PMC article.
-
Non-ammoniagenic proliferation and differentiation media for cultivated adipose tissue.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jul 24;11:1202165. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1202165. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37555077 Free PMC article.
-
Author Correction: Ammonia promotes the proliferation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating the Akt/mTOR/S6k pathway.Bone Res. 2024 Feb 20;12(1):9. doi: 10.1038/s41413-024-00314-y. Bone Res. 2024. PMID: 38378665 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Identification of mesenchymal stem cell populations with high osteogenic potential using difference in cell division rate.Regen Ther. 2025 Feb 4;28:498-508. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2025.01.020. eCollection 2025 Mar. Regen Ther. 2025. PMID: 39991510 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine synthetase regulates the immune microenvironment and cancer development through the inflammatory pathway.Int J Med Sci. 2023 Jan 1;20(1):35-49. doi: 10.7150/ijms.75625. eCollection 2023. Int J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36619229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mariño, G. & Kroemer, G. Ammonia: A diffusible factor released by proliferating cells that induces autophagy. Sci. Signal.3, pe19 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Luo, C. et al. Ammonia drives dendritic cells into dysfunction. J. Immunol. (Baltim., Md.: 1950)193, 1080–1089 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Eng, C. H., Yu, K., Lucas, J., White, E. & Abraham, R. T. Ammonia derived from glutaminolysis is a diffusible regulator of autophagy. Sci. Signal.3, ra31 (2010). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

