Spatially patterned hydrogen peroxide orchestrates stomatal development in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 36028510
- PMCID: PMC9418256
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32770-7
Spatially patterned hydrogen peroxide orchestrates stomatal development in Arabidopsis
Abstract
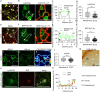
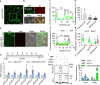
Stomatal pores allow gas exchange between plant and atmosphere. Stomatal development is regulated by multiple intrinsic developmental and environmental signals. Here, we show that spatially patterned hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) plays an essential role in stomatal development. H2O2 is remarkably enriched in meristemoids, which is established by spatial expression patterns of H2O2-scavenging enzyme CAT2 and APX1. SPEECHLESS (SPCH), a master regulator of stomatal development, directly binds to the promoters of CAT2 and APX1 to repress their expression in meristemoid cells. Mutations in CAT2 or APX1 result in an increased stomatal index. Ectopic expression of CAT2 driven by SPCH promoter significantly inhibits the stomatal development. Furthermore, H2O2 activates the energy sensor SnRK1 by inducing the nuclear localization of the catalytic α-subunit KIN10, which stabilizes SPCH to promote stomatal development. Overall, these results demonstrate that the spatial pattern of H2O2 in epidermal leaves is critical for the optimal stomatal development in Arabidopsis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

