Propolis: An update on its chemistry and pharmacological applications
- PMID: 36028892
- PMCID: PMC9412804
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-022-00651-2
Propolis: An update on its chemistry and pharmacological applications
Abstract
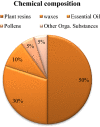
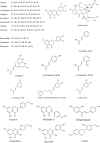
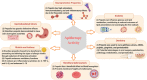
Propolis, a resinous substance produced by honeybees from various plant sources, has been used for thousands of years in traditional medicine for several purposes all over the world. The precise composition of propolis varies according to plant source, seasons harvesting, geography, type of bee flora, climate changes, and honeybee species at the site of collection. This apiary product has broad clinical applications such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticancer, analgesic, antidepressant, and anxiolytic as well asimmunomodulatory effects. It is also well known from traditional uses in treating purulent disorders, improving the wound healing, and alleviating many of the related discomforts. Even if its use was already widespread since ancient times, after the First and Second World War, it has grown even more as well as the studies to identify its chemical and pharmacological features, allowing to discriminate the qualities of propolis in terms of the chemical profile and relative biological activity based on the geographic place of origin. Recently, several in vitro and in vivo studies have been carried out and new insights into the pharmaceutical prospects of this bee product in the management of different disorders, have been highlighted. Specifically, the available literature confirms the efficacy of propolis and its bioactive compounds in the reduction of cancer progression, inhibition of bacterial and viral infections as well as mitigation of parasitic-related symptoms, paving the way to the use of propolis as an alternative approach to improve the human health. However, a more conscious use of propolis in terms of standardized extracts as well as new clinical studies are needed to substantiate these health claims.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Anticancer; Antioxidant; Bee glue; Bioactive compounds; Food preservative.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interest.
Figures








References
-
- Makashvili Z. Remarkable hive product: Propolis. Scientific data and suggestions concerning its composition, properties and possible use in therapeutics. In: From the history of Propolis. APIMONDIA standing commission on Bee keeping technology and equipment, Bucharest. 1978.
-
- Khalil ML. Biological activity of bee propolis in health and disease. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2006;7(1):22–31. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

