Disease severity and efficacy of homologous vaccination among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Delta or Omicron VOCs, compared to unvaccinated using main biomarkers
- PMID: 36029103
- PMCID: PMC9538273
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.28098
Disease severity and efficacy of homologous vaccination among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Delta or Omicron VOCs, compared to unvaccinated using main biomarkers
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum on "Disease severity and efficacy of homologous vaccination among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Delta or Omicron VOCs, compared to unvaccinated using main biomarkers".J Med Virol. 2023 May;95(5):e28824. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28824. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 37226971 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
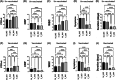
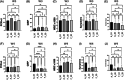
From March 2021, various countries including Iraq issued prompted recommendations for increased COVID-19 vaccine protection in individuals especially those at risk of catching the virus (i.e., lifestyle, health sector workers, and chronic diseases). It is critically important to understand the impact of COVID-19 vaccinations with the most commonly used vaccines (Pfizer and AstraZeneca) among populations either on the severity of the disease or the transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) and in sequential waves. This study was conducted to establish the clinical severity of COVID-19 caused by Delta and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variants among patients who either attended or were admitted to hospitals and to compare the effectiveness of Pfizer and AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccines (single or double doses) at least to prevent hospitalizations if not eradicating the pandemic. A case-control study was done of 570 hospitalized patients; including 328 COVID-19 confirmed patients (166 males, 160 females) who received homologous vaccinations and 242 unvaccinated patients (128 males, 114 females) during the studied waves. The study showed that unvaccinated COVID-19 patients in both waves had expressed significantly a higher number and longer periods of symptoms than vaccinated ones. Additionally, there was no significant effect of vaccine types, Pfizer and AstraZeneca or vaccine shot numbers on the PCR-Ct in the last (Omicron) wave of the pandemic. However, in the previous (Delta) wave of the pandemic, fully vaccinated (double doses) COVID-19 patients had higher PCR-Ct values. Whether among vaccinated or unvaccinated patients, lower CRP levels recorded during the Omicron wave than that of the Delta wave, and regardless of the vaccine type or shot numbers, there were no significant differences between the two waves. Lower WBCs were observed in patients (vaccinated and unvaccinated) infected with the Delta variant in comparison to those infected with the Omicron variant and without any remarkable effect of the vaccine type or shot numbers. This is the first molecular and investigational study of the Delta variant and circulated Omicron in Iraq, regarding the severity of these two waves of SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and the efficacy of homologous vaccination, indicating the insufficiency of two doses and the demand for booster dose(s) as the most effective way of keeping on the safe-side against SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: AstraZeneca; Delta variant; Omicron variant; Pfizer; SARS-CoV-2; homologous vaccination.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Medical Virology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
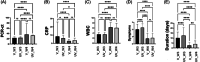
Comment in
-
In response to: Disease severity and efficacy of homologous vaccination among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Delta or Omicron VOCs, compared to unvaccinated using main biomarkers.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28213. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28213. Epub 2022 Oct 17. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36224626 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Letter to the Editor on disease severity and efficacy of homologous vaccination among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Delta or Omicron VOCs, compared to unvaccinated using main biomarkers.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28313. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28313. Epub 2022 Nov 21. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36380449 No abstract available.
-
Response to comments to the editor on "Disease severity and efficacy of homologous vaccination among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Delta or Omicron VOCs, compared to unvaccinated using main biomarkers".J Med Virol. 2023 May;95(5):e28820. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28820. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 37226974 No abstract available.
-
Comments on "Disease severity and efficacy of homologous vaccination among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Delta or Omicron VOCs, compared to unvaccinated using main biomarkers".J Med Virol. 2023 May;95(5):e28822. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28822. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 37231566 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Clinical severity of, and effectiveness of mRNA vaccines against, covid-19 from omicron, delta, and alpha SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States: prospective observational study.BMJ. 2022 Mar 9;376:e069761. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2021-069761. BMJ. 2022. PMID: 35264324 Free PMC article.
-
A Quick Displacement of the SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta with Omicron: Unprecedented Spike in COVID-19 Cases Associated with Fewer Admissions and Comparable Upper Respiratory Viral Loads.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 Jan 28:2022.01.26.22269927. doi: 10.1101/2022.01.26.22269927. medRxiv. 2022. Update in: EBioMedicine. 2022 May;79:104008. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104008. PMID: 35118480 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Association Between 3 Doses of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine and Symptomatic Infection Caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta Variants.JAMA. 2022 Feb 15;327(7):639-651. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.0470. JAMA. 2022. PMID: 35060999 Free PMC article.
-
Role of previous infection with SARS-CoV-2 in protecting against omicron reinfections and severe complications of COVID-19 compared to pre-omicron variants: a systematic review.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Jun 26;23(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08328-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37365490 Free PMC article.
-
The Vaccine Efficacy Against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 13;10:940956. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.940956. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35910897 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In response to: Disease severity and efficacy of homologous vaccination among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Delta or Omicron VOCs, compared to unvaccinated using main biomarkers.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28213. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28213. Epub 2022 Oct 17. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36224626 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A study on the side effects caused by the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine: Focus on IgG antibodies and serological biomarkers.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2024;49(1):2-10. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2024.136382. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38812603 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic polymorphism between the Sorani and Hawrami kurdish populations and COVID-19 outcome.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jun;50(6):5177-5183. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08448-8. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37119412 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of the 4C and SEIMC scoring systems in predicting mortality from onset to current COVID-19 pandemic in emergency departments.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 3;14(1):23009. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73664-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39362962 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the number of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination shots on the occurrence of pneumonia, severe pneumonia, and death in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients.Front Public Health. 2024 Jan 8;11:1330106. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1330106. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38259762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Rolling updates on coronavirus disease. Events as they happen. 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-a.... Accessed July 31, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus disease (COVID‐19) pandemic. 2019. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019. Accessed February 22, 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

