Misfolded protein oligomers induce an increase of intracellular Ca2+ causing an escalation of reactive oxidative species
- PMID: 36030306
- PMCID: PMC9420098
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-022-04513-w
Misfolded protein oligomers induce an increase of intracellular Ca2+ causing an escalation of reactive oxidative species
Abstract
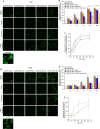
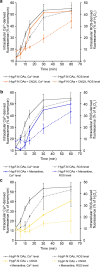
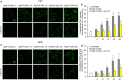
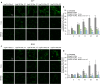
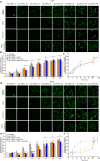
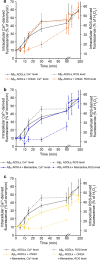
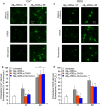
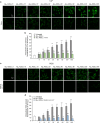
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by the accumulation in the brain of the amyloid β (Aβ) peptide in the form of senile plaques. According to the amyloid hypothesis, the aggregation process of Aβ also generates smaller soluble misfolded oligomers that contribute to disease progression. One of the mechanisms of Aβ oligomer cytotoxicity is the aberrant interaction of these species with the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes, with a consequent increase in cytosolic Ca2+ levels, flowing from the extracellular space, and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Here we investigated the relationship between the increase in Ca2+ and ROS levels immediately after the exposure to misfolded protein oligomers, asking whether they are simultaneous or instead one precedes the other. Using Aβ42-derived diffusible ligands (ADDLs) and type A HypF-N model oligomers (OAs), we followed the kinetics of ROS production and Ca2+ influx in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells and rat primary cortical neurons in a variety of conditions. In all cases we found a faster increase of intracellular Ca2+ than ROS levels, and a lag phase in the latter process. A Ca2+-deprived cell medium prevented the increase of intracellular Ca2+ ions and abolished ROS production. By contrast, treatment with antioxidant agents prevented ROS formation, did not prevent the initial Ca2+ flux, but allowed the cells to react to the initial calcium dyshomeostasis, restoring later the normal levels of the ions. These results reveal a mechanism in which the entry of Ca2+ causes the production of ROS in cells challenged by aberrant protein oligomers.
Keywords: AMPA receptors; Calcium homeostasis; Membrane destabilization; NMDA receptors; Neurodegenerative diseases; Oxidative stress; Protein misfolding.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aβ Oligomers Dysregulate Calcium Homeostasis by Mechanosensitive Activation of AMPA and NMDA Receptors.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021 Feb 17;12(4):766-781. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00811. Epub 2021 Feb 4. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33538575 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate attenuates neuronal dysfunction induced by amyloid-β oligomers through endocytic internalization of NMDA receptors.FEBS J. 2023 Jan;290(1):112-133. doi: 10.1111/febs.16579. Epub 2022 Aug 12. FEBS J. 2023. PMID: 35851748 Free PMC article.
-
Abeta oligomers induce neuronal oxidative stress through an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent mechanism that is blocked by the Alzheimer drug memantine.J Biol Chem. 2007 Apr 13;282(15):11590-601. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607483200. Epub 2007 Feb 16. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17308309
-
Vicious cycles within the neuropathophysiologic mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2006 Apr;3(2):95-108. doi: 10.2174/156720506776383068. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2006. PMID: 16611010 Review.
-
Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Amyloid-β in Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2019;16(5):418-452. doi: 10.2174/1567205016666190321163438. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2019. PMID: 30907320 Review.
Cited by
-
Egg exosome miR-145-5p decreases mitochondrial ROS to protect chicken embryo hepatocytes against apoptosis through targeting MAPK10.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025 May 24;16(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s40104-025-01203-y. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40410809 Free PMC article.
-
A single-domain antibody detects and neutralises toxic Aβ42 oligomers in the Alzheimer's disease CSF.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Jan 18;16(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01361-z. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38238842 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Attribution of the Protective Effects of Aminosterols against Protein Aggregates to Their Chemical Structures and Ability to Modulate Biological Membranes.J Med Chem. 2023 Jul 27;66(14):9519-9536. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00182. Epub 2023 Jul 11. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37433124 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Pairs of Toxic and Nontoxic Misfolded Protein Oligomers Elucidates the Structural Determinants of Oligomer Toxicity in Protein Misfolding Diseases.Acc Chem Res. 2023 Jun 20;56(12):1395-1405. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00045. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Acc Chem Res. 2023. PMID: 37071750 Free PMC article.
-
Putative novel CSF biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease based on the novel concept of generic protein misfolding and proteotoxicity: the PRAMA cohort.Transl Neurodegener. 2024 Mar 8;13(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s40035-024-00405-0. Transl Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 38459525 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

