Refining the definition of HER2-low class in invasive breast cancer
- PMID: 36030496
- PMCID: PMC9826019
- DOI: 10.1111/his.14780
Refining the definition of HER2-low class in invasive breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Emerging evidence indicates that breast cancer (BC) patients whose tumours express HER2 protein without HER2 gene amplification (HER2-low), can benefit from antibody-drug conjugates (ADC). However, the current definition of HER2-low BC remains incomplete with low rates of concordance. This study aims to refine HER2-low definition with emphasis on distinguishing HER2 score 0 from score 1+ to identify patients who are eligible for ADC.
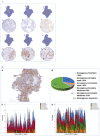
Methods: A BC cohort (n = 363) with HER2 IHC scores 0, 1+ and 2+ (without HER2 gene amplification) and available HER2 mRNA was included. HER2 staining intensity, pattern and subcellular localisation were reassessed. Artificial neural network analysis was applied to cluster the cohort and to distinguish HER2 score 0 from 1+. Reproducibility and reliability of the refined criteria were tested.
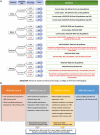
Results: HER2 IHC score 1+ was refined as membranous staining in invasive cells as either: (1) faint intensity in ≥ 20% of cells regardless the circumferential completeness, (2) weak complete staining in ≤ 10%, (3) weak incomplete staining in > 10% and (4) moderate incomplete staining in ≤ 10%. Based on this, 63% of the HER2-negative cases were reclassified as positive (HER2-low). The refined score showed perfect observer agreement compared to the moderate agreement in the original clinical scores. Similar results were generated when the refined score was applied on the independent BC cohorts. A proposal to refine the definition of other HER2 classes is presented.
Conclusion: This study refined the definition of HER2-low BC based on correlation with HER2 mRNA and distinguished between HER2 IHC score 1+ and score 0 tumours.
Keywords: ANN; HER2 low; HER2 mRNA; breast cancer; refining.
© 2022 The Authors. Histopathology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Marchiò C, Annaratone L, Marques A, Casorzo L, Berrino E, Sapino A, editors. Evolving concepts in HER2 evaluation in breast cancer: Heterogeneity, HER2‐low carcinomas and beyond. Seminars in cancer biology; 2021: Elsevier. - PubMed
-
- Harbeck N, Gnant M. Interpretation of the evidence for the efficacy and safety of statin therapy. Lancet 2017; 389; 1134–1150. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

