Breathing disturbances in Rett syndrome
- PMID: 36031301
- PMCID: PMC10029146
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-323-91532-8.00018-5
Breathing disturbances in Rett syndrome
Abstract
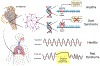
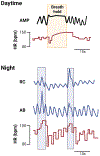
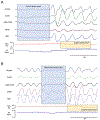
Rett Syndrome is an X-linked neurological disorder characterized by behavioral and neurological regression, seizures, motor deficits, and dysautonomia. A particularly prominent presentation includes breathing abnormalities characterized by breathing irregularities, hyperventilation, repetitive breathholding during wakefulness, obstructive and central apneas during sleep, and abnormal responses to hypoxia and hypercapnia. The condition and pathology of the respiratory system is further complicated by dysfunctions of breathing-motor coordination, which is reflected in dysphagia. The discovery of the X-linked mutations in the MECP2 gene has transformed our understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms that are at the root of various clinical phenotypes. However, the genotype-phenotype relationship is complicated by various factors which include not only X-inactivation but also consequences of the intermittent hypoxia and oxidative stress associated with the breathing abnormalities.
Keywords: Apnea; Breathing; Rett Syndrome.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Athar M, Lloyd JR, Bickers DR, Mukhtar H. Malignant conversion of UV radiation and chemically induced mouse skin benign tumors by free-radical-generating compounds. Carcinogenesis. 1989;10(10):1841–5. - PubMed
-
- Rett A. [On a unusual brain atrophy syndrome in hyperammonemia in childhood]. Wiener medizinische Wochenschrift (1946). 1966;116(37):723–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

