IL-2 receptor engineering enhances regulatory T cell function suppressed by calcineurin inhibitor
- PMID: 36031344
- PMCID: PMC10184573
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.17181
IL-2 receptor engineering enhances regulatory T cell function suppressed by calcineurin inhibitor
Abstract
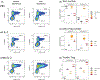
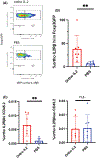
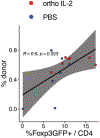
Clinical trials utilizing regulatory T cell (Treg) therapy in organ transplantation have shown promising results, however, the choice of a standard immunosuppressive regimen is still controversial. Calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs) are one of the most common immunosuppressants for organ transplantation, although they may negatively affect Tregs by inhibiting IL-2 production by conventional T cells. As a strategy to replace IL-2 signaling selectively in Tregs, we have introduced an engineered orthogonal IL-2 (ortho IL-2) cytokine/cytokine receptor (R) pair that specifically binds with each other but does not bind with their wild-type counterparts. Murine Tregs were isolated from recipients and retrovirally transduced with ortho IL-2Rβ during ex vivo expansion. Transduced Tregs (ortho Tregs) were transferred into recipient mice in a mixed hematopoietic chimerism model with tacrolimus administration. Ortho IL-2 treatment significantly increased the ortho IL-2Rβ(+) Treg population in the presence of tacrolimus without stimulating other T cell subsets. All the mice treated with tacrolimus plus ortho IL-2 achieved heart allograft tolerance, even after tacrolimus cessation, whereas those receiving tacrolimus treatment alone did not. These data demonstrate that Treg therapy can be adopted into a CNI-based regimen by utilizing cytokine receptor engineering.
Keywords: animal models: murine; basic (laboratory) research/science; bioengineering; cellular biology; cytokines/cytokine receptors; immunobiology; immunosuppressant - calcineurin inhibitor (CNI); immunosuppression/immune modulation; tolerance: chimerism.
© 2022 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE
The authors of this manuscript have conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the
Figures
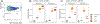


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

