Effect of Repeat Vaccination on Immunogenicity of Quadrivalent Cell-Culture and Recombinant Influenza Vaccines Among Healthcare Personnel Aged 18-64 Years: A Randomized, Open-Label Trial
- PMID: 36031405
- PMCID: PMC9907492
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciac683
Effect of Repeat Vaccination on Immunogenicity of Quadrivalent Cell-Culture and Recombinant Influenza Vaccines Among Healthcare Personnel Aged 18-64 Years: A Randomized, Open-Label Trial
Abstract
Background: Antibody responses to non-egg-based standard-dose cell-culture influenza vaccine (containing 15 µg hemagglutinin [HA]/component) and recombinant vaccine (containing 45 µg HA/component) during consecutive seasons have not been studied in the United States.
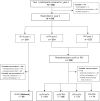
Methods: In a randomized trial of immunogenicity of quadrivalent influenza vaccines among healthcare personnel (HCP) aged 18-64 years over 2 consecutive seasons, HCP who received recombinant-HA influenza vaccine (RIV) or cell culture-based inactivated influenza vaccine (ccIIV) during the first season (year 1) were re-randomized the second season of 2019-2020 (year 2 [Y2]) to receive ccIIV or RIV, resulting in 4 ccIIV/RIV combinations. In Y2, hemagglutination inhibition antibody titers against reference cell-grown vaccine viruses were compared in each ccIIV/RIV group with titers among HCP randomized both seasons to receive egg-based, standard-dose inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV) using geometric mean titer (GMT) ratios of Y2 post-vaccination titers.
Results: Y2 data from 414 HCP were analyzed per protocol. Compared with 60 IIV/IIV recipients, 74 RIV/RIV and 106 ccIIV/RIV recipients showed significantly elevated GMT ratios (Bonferroni corrected P < .007) against all components except A(H3N2). Post-vaccination GMT ratios for ccIIV/ccIIV and RIV/ccIIV were not significantly elevated compared with IIV/IIV except for RIV/ccIIV against A(H1N1)pdm09.
Conclusions: In adult HCP, receipt of RIV in 2 consecutive seasons or the second season was more immunogenic than consecutive egg-based IIV for 3 of the 4 components of quadrivalent vaccine. Immunogenicity of ccIIV/ccIIV was similar to that of IIV/IIV. Differences in HA antigen content may play a role in immunogenicity of influenza vaccination in consecutive seasons.
Clinical trials registration: NCT03722589.
Keywords: Flublok Quadrivalent; Flucelvax Quadrivalent; healthcare personnel; immunogenicity; influenza vaccines.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. M. G. reports grants from the unrelated CDC (US Ambulatory Flu/COVID Vaccine Effectiveness Network, Hospitalized Adult Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network [HAIVEN], Refining Effectiveness Estimates of Influenza Vaccines Synergizing Epidemiolgy and Incidence Methods for Influenza and Other Acute Respiratory Viral Illness [SYNERGY] Studies), unrelated CDC-Abt Associates (Research on the Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Essential Response Personnel [RECOVER] and Pediatric Research Observing Trends and Exposures in COVID-19 Timelines [PROTECT] cohort studies), unrelated CDC–Vanderbilt University Medical Center (Influenza and Other Viruses in the Acutely Ill [IVY] Study), unrelated CDC-Westat (Virtual Network: Investigating the Risk of COVID-19-Associated Outcomes and COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness Using Integrated Medical and Public Health Records [VISION-COVID] Study), unrelated Janssen (RSV Severity Birth Cohort Study), and unrelated Pfizer (Education for Men B Vaccine in Adolescents); being the co-chair of the Texas Pediatric Society's (Texas Chapter of the American Academy of Pediatrics) Infectious Diseases and Immunization Committee (2016–2022). A. L. N. reports funding from Pfizer and Vir Biotechnology for unrelated studies. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recombinant quadrivalent influenza vaccine (RIV) induces robust cell-mediated and HA-specific B cell humoral immune responses among healthcare personnel.Vaccine. 2025 Jun 19;61:127361. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2025.127361. Online ahead of print. Vaccine. 2025. PMID: 40540779 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody response to sequential vaccination with cell culture, recombinant, or egg-based influenza vaccines among U.S. adults.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2370087. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2370087. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38982712 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the Immunogenicity of Cell Culture-Based and Recombinant Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccines to Conventional Egg-Based Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccines Among Healthcare Personnel Aged 18-64 Years: A Randomized Open-Label Trial.Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Dec 6;73(11):1973-1981. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab566. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34245243 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Priming with MF59 adjuvanted versus nonadjuvanted seasonal influenza vaccines in children - A systematic review and a meta-analysis.Vaccine. 2020 Jan 16;38(3):608-619. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.10.053. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 31735505
-
Association between vaccine adjuvant effect and pre-seasonal immunity. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised immunogenicity trials comparing squalene-adjuvanted and aqueous inactivated influenza vaccines.Vaccine. 2020 Feb 11;38(7):1614-1622. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.12.037. Epub 2019 Dec 24. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 31879122
Cited by
-
Redirecting antibody responses from egg-adapted epitopes following repeat vaccination with recombinant or cell culture-based versus egg-based influenza vaccines.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 4;15(1):254. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44551-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38177116 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Randomised immunogenicity trial comparing 2019-2020 recombinant and egg-based influenza vaccines among frequently vaccinated healthcare personnel in Israel.Int J Infect Dis. 2024 Dec;149:107260. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2024.107260. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Int J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39395753 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Recombinant quadrivalent influenza vaccine (RIV) induces robust cell-mediated and HA-specific B cell humoral immune responses among healthcare personnel.Vaccine. 2025 Jun 19;61:127361. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2025.127361. Online ahead of print. Vaccine. 2025. PMID: 40540779 Free PMC article.
-
Production, Passaging Stability, and Histological Analysis of Madin-Darby Canine Kidney Cells Cultured in a Low-Serum Medium.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;12(9):991. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12090991. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39340023 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of High-Dose Egg-Based, Recombinant, and Cell Culture-Based Influenza Vaccines Compared With Standard-Dose Egg-Based Influenza Vaccine Among Health Care Personnel Aged 18-65 Years in 2019-2020.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023 Apr 21;10(6):ofad223. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofad223. eCollection 2023 Jun. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37305842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Immunization of health-care personnel: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep 2011; 60(RR-7):1–45. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Influenza vaccination coverage among health care personnel—United States, 2019–20 influenza season. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/fluvaxview/hcp-coverage_1920estimates.htm. Accessed 9 April 2022.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Flu vaccination coverage, United States, 2019–20 influenza season. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/fluvaxview/coverage-1920estimates. Accessed 9 April 2022.
-
- Gambaryan AS, Robertson JS, Matrosovich MN. Effects of egg-adaptation on the receptor-binding properties of human influenza A and B viruses. Virology 1999; 258:232–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

