Tonsillar Microbiome-Derived Lantibiotics Induce Structural Changes of IL-6 and IL-21 Receptors and Modulate Host Immunity
- PMID: 36031409
- PMCID: PMC9596850
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202202706
Tonsillar Microbiome-Derived Lantibiotics Induce Structural Changes of IL-6 and IL-21 Receptors and Modulate Host Immunity
Abstract
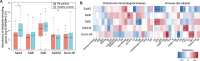
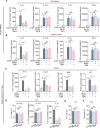
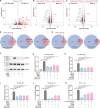
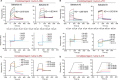
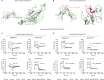
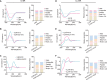
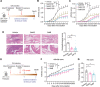
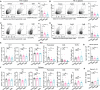
Emerging evidence emphasizes the functional impacts of host microbiome on the etiopathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, there are limited mechanistic insights into the contribution of microbial biomolecules especially microbial peptides toward modulating immune homeostasis. Here, by mining the metagenomics data of tonsillar microbiome, a deficiency of the encoding genes of lantibiotic peptides salivaricins in RA patients is identified, which shows strong correlation with circulating immune cells. Evidence is provided that the salivaricins exert immunomodulatory effects in inhibiting T follicular helper (Tfh) cell differentiation and interleukin-21 (IL-21) production. Mechanically, salivaricins directly bind to and induce conformational changes of IL-6 and IL-21 receptors, thereby inhibiting the bindings of IL-6 and IL-21 to their receptors and suppressing the downstream signaling pathway. Finally, salivaricin administration exerts both prophylactic and therapeutic effects against experimental arthritis in a murine model of RA. Together, these results provide a mechanism link of microbial peptides-mediated immunomodulation.
Keywords: IL-6 and IL-21 receptor; lantibiotics; rheumatoid arthritis; salivaricins; tonsillar microbiome.
© 2022 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- a) Ruff W. E., Greiling T. M., Kriegel M. A., Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 521; - PubMed
- b) Schluter J., Peled J. U., Taylor B. P., Markey K. A., Smith M., Taur Y., Niehus R., Staffas A., Dai A., Fontana E., Amoretti L. A., Wright R. J., Morjaria S., Fenelus M., Pessin M. S., Chao N. J., Lew M., Bohannon L., Bush A., Sung A. D., Hohl T. M., Perales M. A., van den Brink M. R. M., Xavier J. B., Nature 2020, 588, 303. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Skelly A. N., Sato Y., Kearney S., Honda K., Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 305. - PubMed
-
- Zaiss M. M., Joyce Wu H. J., Mauro D., Schett G., Ciccia F., Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 224. - PubMed
-
- Smolen J. S., Aletaha D., Barton A., Burmester G. R., Emery P., Firestein G. S., Kavanaugh A., McInnes I. B., Solomon D. H., Strand V., Yamamoto K., Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18001. - PubMed
-
- a) Abdollahi‐Roodsaz S., Joosten L. A., Koenders M. I., Devesa I., Roelofs M. F., Radstake T. R., Heuvelmans‐Jacobs M., Akira S., Nicklin M. J., Ribeiro‐Dias F., van den W. B., Berg, J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 205; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Teng F., Klinger C. N., Felix K. M., Bradley C. P., Wu E., Tran N. L., Umesaki Y., Wu H. J., Immunity 2016, 44, 875; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Maeda Y., Kurakawa T., Umemoto E., Motooka D., Ito Y., Gotoh K., Hirota K., Matsushita M., Furuta Y., Narazaki M., Sakaguchi N., Kayama H., Nakamura S., Iida T., Saeki Y., Kumanogoh A., Sakaguchi S., Takeda K., Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U1903210/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81901648/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81801618/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81771743/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32141004/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Z191100006619109/Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission
- PKU2021LCXQ008/Clinical Medicine Plus X-Young Scholars Project of Peking University, supported by "the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- XDB29020000/Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
- Z191100006619114/Beijing Science and Technology Program
- 0094/2018/A3/Macao Science and Technology Fund
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
