A data-driven approach finds RNA polymerase III antibody and tendon friction rubs as enrichment tools for early diffuse scleroderma trials
- PMID: 36031807
- PMCID: PMC10072884
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac501
A data-driven approach finds RNA polymerase III antibody and tendon friction rubs as enrichment tools for early diffuse scleroderma trials
Abstract
Objective: Clinical trials in early diffuse SSc have consistently shown a placebo group response with a declining modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS), with negative outcomes. Our objective was to identify strategies using clinical characteristics or laboratory values to improve trial design.
Methods: We identified early diffuse SSc patients first seen at the University of Pittsburgh from 1980-2015. Eligible patients had ≥3 visits, with at least two mRSS scores within the first year of follow-up. We performed Kaplan-Meier analyses, group-based trajectory analysis of mRSS scores, followed by multivariable regression analysis and classification tree analysis. We applied the results to the abatacept in early diffuse systemic sclerosis (ASSET) trial outcome data.
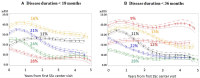
Results: We identified 403 patients with <18 months, and 514 with <36 months disease duration. The median number of mRSS follow-up scores was 14 (interquartile range 8, 25). All methodologic approaches identified skin thickness progression rate, RNA polymerase III (RNAP3) antibody positivity and presence of tendon friction rubs (TFR) as predictors of mRSS trajectory over 5 years of follow-up, and thereby as potential enrichment variables. When applied to the ASSET data, adjustment for both RNAP3 and TFR demonstrated reduction of the placebo mRSS response, particularly at 6 months. A significant difference in the ACR Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS) score was found with adjustment by RNAP3 at 6 months, and TFR or RNAP3 at 12 months.
Conclusion: Adjustment for both RNAP3 and TFR predicts mRSS trajectory and diminished the mRSS decline in ASSET placebo group, and identified significant differences in CRISS. RNAP3, particularly, is a stratification or enrichment approach to improve early diffuse SSc trial design.
Keywords: SSc; clinical trial design; early diffuse scleroderma; scleroderma.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tendon friction rubs in early diffuse systemic sclerosis: prevalence, characteristics and longitudinal changes in a randomized controlled trial.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010 May;49(5):955-9. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep464. Epub 2010 Feb 9. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010. PMID: 20144926 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of Scleroderma-Associated Autoantibodies on Clinical Outcome Assessments: Post Hoc Analysis From a Randomised, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Phase 3 Trial of Tocilizumab in Scleroderma.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2025 Jan;7(1):e11782. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11782. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39846245 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of improvement in skin fibrosis in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: a EUSTAR analysis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2016 Oct;75(10):1743-8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208024. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 27016052 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of cyclophosphamide for skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis: a systematic review and single-arm meta-analysis.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;81(6):863-874. doi: 10.1007/s00228-025-03837-3. Epub 2025 Apr 8. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40198334
-
Challenges in systemic sclerosis trial design.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Dec;49(3S):S3-S7. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.09.019. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019. PMID: 31779848 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell analysis reveals key differences between early-stage and late-stage systemic sclerosis skin across autoantibody subgroups.Ann Rheum Dis. 2023 Dec;82(12):1568-1579. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-224184. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023. PMID: 37580109 Free PMC article.
-
Hand Swelling and Other Non-Raynaud Phenomenon Symptoms as the Initial Presentation of Systemic Sclerosis: Prevalence and Clinical Associations in Two US Cohorts.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025 May 19:10.1002/art.43237. doi: 10.1002/art.43237. Online ahead of print. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40386907
-
Recent Advances in Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis and Morphea.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2024 Mar;25(2):213-226. doi: 10.1007/s40257-023-00831-2. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38087156 Review.
References
-
- Bryan C, Knight C, Black CM, Silman AJ.. Prediction of five-year survival following presentation with scleroderma: development of a simple model using three disease factors at first visit. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:2660–5. - PubMed
-
- Barnett AJ, Miller MH, Littlejohn GO.. A survival study of patients with scleroderma diagnosed over 30 years (1953-1983): the value of a simple cutaneous classification in the early stages of the disease. J Rheumatol 1988;15:276–83. - PubMed
-
- Ferri C, Valentini G, Cozzi F. et al.; Systemic Sclerosis Study Group of the Italian Society of Rheumatology (SIR-GSSSc). Systemic sclerosis: demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in 1,012 Italian patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2002;81:139–53. - PubMed
-
- Scussel-Lonzetti LJ, Raynauld JP, Roussin A. et al. Predicting mortality in systemic sclerosis: analysis of a cohort of 309 French Canadian patients with emphasis on features at diagnosis as predictive factors for survival. Medicine (Baltimore) 2002;81:154–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

