IFN-γ, should not be ignored in SLE
- PMID: 36032079
- PMCID: PMC9399831
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.954706
IFN-γ, should not be ignored in SLE
Abstract
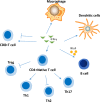
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a typical autoimmune disease with a complex pathogenesis and genetic predisposition. With continued understanding of this disease, it was found that SLE is related to the interferon gene signature. Most studies have emphasized the important role of IFN-α in SLE, but our previous study suggested a nonnegligible role of IFN-γ in SLE. Some scholars previously found that IFN-γ is abnormally elevated as early as before the classification of SLE and before the emergence of autoantibodies and IFN-α. Due to the large overlap between IFN-α and IFN-γ, SLE is mostly characterized by expression of the IFN-α gene after onset. Therefore, the role of IFN-γ in SLE may be underestimated. This article mainly reviews the role of IFN-γ in SLE and focuses on the nonnegligible role of IFN-γ in SLE to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the disease.
Keywords: IFN-γ; autoimmune; biologic therapy; immune cells; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang S-Y, Boisson-Dupuis S, Chapgier A, Yang K, Bustamante J, Puel A, et al. Inborn errors of interferon (IFN)-mediated immunity in humans: insights into the respective roles of IFN-alpha/beta, IFN-gamma, and IFN-lambda in host defense. Immunol Rev (2008) 226:29–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00698.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

