Insulin B-chain hybrid peptides are agonists for T cells reactive to insulin B:9-23 in autoimmune diabetes
- PMID: 36032090
- PMCID: PMC9399855
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.926650
Insulin B-chain hybrid peptides are agonists for T cells reactive to insulin B:9-23 in autoimmune diabetes
Abstract
Insulin is considered to be a key antigenic target of T cells in Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) and autoimmune diabetes in the NOD mouse with particular focus on the B-chain amino acid sequence B:9-23 as the primary epitope. Our lab previously discovered that hybrid insulin peptides (HIPs), comprised of insulin C-peptide fragments fused to other β-cell granule peptides, are ligands for several pathogenic CD4 T cell clones derived from NOD mice and for autoreactive CD4 T cells from T1D patients. A subset of CD4 T cell clones from our panel react to insulin and B:9-23 but only at high concentrations of antigen. We hypothesized that HIPs might also be formed from insulin B-chain sequences covalently bound to other endogenously cleaved ß-cell proteins. We report here on the identification of a B-chain HIP, termed the 6.3HIP, containing a fragment of B:9-23 joined to an endogenously processed peptide of ProSAAS, as a strong neo-epitope for the insulin-reactive CD4 T cell clone BDC-6.3. Using an I-Ag7 tetramer loaded with the 6.3HIP, we demonstrate that T cells reactive to this B-chain HIP can be readily detected in NOD mouse islet infiltrates. This work suggests that some portion of autoreactive T cells stimulated by insulin B:9-23 may be responding to B-chain HIPs as peptide ligands.
Keywords: B:9-23; HIPS; NOD mouse; T cell; autoimmune diabetes; insulin; type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Wenzlau, DiLisio, Barbour, Dang, Hohenstein, Nakayama, Delong, Baker and Haskins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

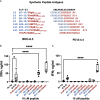


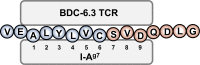
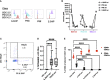
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

