The relationship between dyslipidemia and inflammation among adults in east coast China: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 36032093
- PMCID: PMC9403313
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.937201
The relationship between dyslipidemia and inflammation among adults in east coast China: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Objective: Dyslipidemia is one of the major public health problems in China. It is characterized by multisystem dysregulation and inflammation, and oxidant/antioxidant balance has been suggested as an important factor for its initiation and progression. The objective of this study was to determine the relationship between prevalence of dyslipidemia and measured changes in the levels of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-a, and MCP-1), thiobarbituric acid-reactant substances (TBARS), and serum total antioxidant capacity (TAC) in serum samples.
Study design: A cross-sectional survey with a purposive sampling of 2,631 enrolled participants (age 18-85 years) was performed using the adult population of long-term residents of the municipality of east coast China in Fujian province between the years 2017 and 2019. Information on general health status, dyslipidemia prevalence, and selected mediators of inflammation was collected through a two-stage probability sampling design according to socioeconomic level, sex, and age.
Methods: The lipid profile was conducted by measuring the levels of total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and triglycerides (TG) with an autoanalyzer. Dyslipidemia was defined according to National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III diagnostic criteria, and patients with it were identified by means of a computerized database. Serum parameters including IL-6/TNF-a/MCP-1, TBARS, and TAC were measured in three consecutive years. Familial history, education level, risk factors, etc. were determined. The association between dyslipidemia and serum parameters was explored using multivariable logistic regression models. Sociodemographic, age, and risk factors were also investigated among all participants.
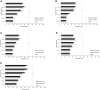
Results: The mean prevalence of various dyslipidemia in the population at baseline (2017) was as follows: dyslipidemias, 28.50%; hypercholesterolemia, 26.33%; high LDL-C, 26.10%; low HDL-C, 24.44%; and hypertriglyceridemia, 27.77%. A significant effect of aging was found among all male and female participants. The mean levels of serum Il-6/TNF-a/MCP-1 were significantly higher in all the types of dyslipidemia among male participants. Female participants with all types of dyslipidemia but low HDL-C showed an elevation of IL-6 and MCP-1 levels, and those with dyslipidemias and hypercholesterolemia presented higher levels of TNF-a compared to the normal participants. The oxidative stress marker TBARS increased among all types of dyslipidemia except hypertriglyceridemia. All participants with different types of dyslipidemia had a lower total antioxidant capacity. Correlation analysis showed that cytokines and TBARS were positively associated with age, obesity, and diabetes mellitus, but not sex, sedentary leisure lifestyle, hypertension, and CVD/CHD history. The activity of TAC was negatively associated with the above parameters.
Conclusions: The correlation between the prevalence of dyslipidemia and the modification of inflammation status was statistically significant. The levels of proinflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress, and antioxidant capacity in serum may reflect the severity of the lipid abnormalities. These promising results further warrant a thorough medical screening in enhanced anti-inflammatory and reduced oxidative stress to better diagnose and comprehensively treat dyslipidemia at an early stage.
Keywords: IL-6; MCP-1; TAC; TBARS; TNF-a; dyslipidemia.
Copyright © 2022 Hong, Lin, Ye, Yang, Huang, Duan and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
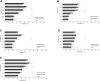
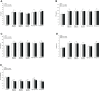

Similar articles
-
Prevalence of dyslipidemia and associated risk factors among Turkish adults: Trabzon lipid study.Endocrine. 2008 Aug-Dec;34(1-3):36-51. doi: 10.1007/s12020-008-9100-z. Epub 2008 Nov 12. Endocrine. 2008. PMID: 19003544
-
Prevalence and factors associated with dyslipidemia in Bangladeshi adults.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 20;18(1):e0280672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280672. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36662845 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Profile and the Frequency of Dyslipidemia in Iranian Adolescents with Severe Obesity, Who Were Candidates for Bariatric Surgery.Obes Surg. 2024 Feb;34(2):618-624. doi: 10.1007/s11695-023-07038-8. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Obes Surg. 2024. PMID: 38191967
-
Nutrition interventions for adults with dyslipidemia: A Clinical Perspective from the National Lipid Association.J Clin Lipidol. 2023 Jul-Aug;17(4):428-451. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2023.05.099. Epub 2023 Jun 2. J Clin Lipidol. 2023. PMID: 37271600 Review.
-
Dyslipidemias in patients with diabetes mellitus: classification and risks and benefits of therapy.Pharmacotherapy. 1995 May-Jun;15(3):317-37. Pharmacotherapy. 1995. PMID: 7667166 Review.
Cited by
-
Unravelling the ties that bind: The intersection of obesity, osteoarthritis, and inflammatory pathways with emphasis on glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists.Clin Obes. 2025 Feb;15(1):e12700. doi: 10.1111/cob.12700. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Clin Obes. 2025. PMID: 39152660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Intensity Interval Training Enhances the Positive Effect of Pentoxifylline on Lipid Profile and Inflammatory Markers in an Endometriosis Animal Model.Biomed Res Int. 2025 Mar 10;2025:6742953. doi: 10.1155/bmri/6742953. eCollection 2025. Biomed Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40224541 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of age on outcomes and hospital costs of urgent laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Surg. 2025 May 24;25(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s12893-025-02963-0. BMC Surg. 2025. PMID: 40413471 Free PMC article.
-
Non-linear connection between the triglyceride-glucose index and prediabetes risk among Chinese adults: a secondary retrospective cohort study.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Nov 5;29(1):529. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02121-x. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39497216 Free PMC article.
-
NPC1L1 rs217434 A > G as a Novel Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Related to Dyslipidemia in a Korean Population.Biochem Genet. 2024 Oct;62(5):4103-4119. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10649-6. Epub 2024 Jan 27. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 38280151
References
-
- Eisen A, Tenenbaum A, Koren-Morag N, Tanne D, Shemesh J, Imazio M, et al. . Calcification of the thoracic aorta as detected by spiral computed tomography among stable angina pectoris patients: Association with cardiovascular events and death. Circulation (2008) 118(13):1328–34. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.712141 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

