Complement lectin pathway components MBL and MASP-1 promote haemostasis upon vessel injury in a microvascular bleeding model
- PMID: 36032172
- PMCID: PMC9412763
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.948190
Complement lectin pathway components MBL and MASP-1 promote haemostasis upon vessel injury in a microvascular bleeding model
Abstract
Background: Complement lectin pathway components, in particular mannan-binding lectin (MBL) and MBL-associated serine proteases (MASPs) have been shown to interact with coagulation factors and contribute to clot formation. Here we investigated the role of MBL and MASP-1 in the haemostatic response following mechanical vessel injury in a human microfluidic bleeding model.
Methods: We studied haemostasis in a microvascular bleeding model in the presence of human endothelial cells and human whole blood under flow conditions. We monitored incorporation of proteins into the clot with fluorescently labelled antibodies and studied their effects on clot formation, platelet activation, and bleeding time with specific inhibitors. Platelet activation was also studied by flow cytometry.
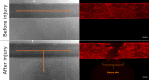
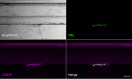
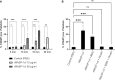
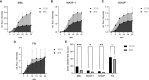
Results: Upon vessel injury, MBL accumulated at the injury site in a well-defined wall-like structure. MBL showed partial colocalisation with fibrin, and strong colocalisation with von Willebrand factor and (activated) platelets. Flow cytometry ruled out direct binding of MBL to platelets, but confirmed a PAR4- and thrombin-dependent platelet-activating function of MASP-1. Inhibiting MBL during haemostasis reduced platelet activation, while inhibiting MASP-1 reduced platelet activation, fibrin deposition and prolonged bleeding time.
Conclusion: We show in a microvascular human bleeding model that MBL and MASP-1 have important roles in the haemostatic response triggered by mechanical vessel injury: MBL recognises the injury site, while MASP-1 increases fibrin formation, platelet activation and shortens bleeding time. While the complement lectin pathway may be harmful in the context of pathological thrombosis, it appears to be beneficial during the physiological coagulation response by supporting the crucial haemostatic system.
Keywords: MBL-associated serine protease-1 (MASP-1); complement system; haemostasis; mannan-binding lectin (MBL); microfluidics.
Copyright © 2022 Golomingi, Kohler, Jenny, Hardy, Dobó, Gál, Pál, Kiss, Lam and Schroeder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Complement inhibition can decrease the haemostatic response in a microvascular bleeding model at multiple levels.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 13;14:1226832. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1226832. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37771595 Free PMC article.
-
The lectin complement pathway serine proteases (MASPs) represent a possible crossroad between the coagulation and complement systems in thromboinflammation.J Thromb Haemost. 2016 Mar;14(3):531-45. doi: 10.1111/jth.13208. Epub 2016 Feb 15. J Thromb Haemost. 2016. PMID: 26614707
-
Activation of mannan-binding lectin-associated serine proteases leads to generation of a fibrin clot.Immunology. 2010 Apr;129(4):482-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03200.x. Epub 2009 Dec 2. Immunology. 2010. PMID: 20002787 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging roles of mannose-binding lectin-associated serine proteases (MASPs) in the lectin pathway of complement and beyond.Immunol Rev. 2016 Nov;274(1):98-111. doi: 10.1111/imr.12460. Immunol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27782318 Review.
-
A journey through the lectin pathway of complement-MBL and beyond.Immunol Rev. 2016 Nov;274(1):74-97. doi: 10.1111/imr.12468. Immunol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27782323 Review.
Cited by
-
Complement inhibition can decrease the haemostatic response in a microvascular bleeding model at multiple levels.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 13;14:1226832. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1226832. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37771595 Free PMC article.
-
Hemostasis-on-a-chip / incorporating the endothelium in microfluidic models of bleeding.Platelets. 2023 Dec;34(1):2185453. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2023.2185453. Platelets. 2023. PMID: 36872890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of immune cells in organs-on-chips: a tutorial.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jun 1;11:1191104. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1191104. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37324438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Lectin Pathway of the Complement System-Activation, Regulation, Disease Connections and Interplay with Other (Proteolytic) Systems.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 26;25(3):1566. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031566. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

