Detection of bla OXA-145, bla OXA-224, bla OXA-539, and bla OXA-675 Genes and Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Class D β-Lactamases (CHDLs) in Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Collected from West of Iran, Hamadan
- PMID: 36032180
- PMCID: PMC9411009
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3841161
Detection of bla OXA-145, bla OXA-224, bla OXA-539, and bla OXA-675 Genes and Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Class D β-Lactamases (CHDLs) in Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Collected from West of Iran, Hamadan
Abstract
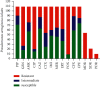
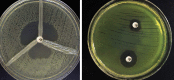
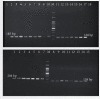
Carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D β-lactamases (CHDLs) are on the rise and are a major public health problem worldwide. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is resistant to carbapenem; currently, the most effective treatment option is being increasingly reported. This study aimed to identify blaOXA-145, blaOXA-224, blaOXA-539, and blaOXA-675 genes in CHDL strains. Samples were collected from clinical specimens admitted to the hospital. Antibiotic susceptibility was determined using the disk diffusion methods. CHDL strains were detected using a phenotypic method (disk diffusion). The PCR method was used to identify blaOXA-145, blaOXA-224, blaOXA-539, and blaOXA-675 genes. Piperacillin-resistant strains (n = 9, 17.4%) had the lowest frequency, and cefoxitin-resistant strains (n = 100, 91.7%) had the highest distribution in P. aeruginosa isolates. Also, 29.35%, 12.8%, and 8.2% were multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant, and pan drug-resistant, respectively. MBL-producing P. aeruginosa and KPC-producing P. aeruginosa were detected, respectively, in 47.7% and 37.6% of isolates. Biofilm formation was observed in 63.3% of P. aeruginosa isolates. The frequency of OXA genes was as follows: blaOXA-145 gene in 30 isolates (27.5%), blaOXA-224 in 24 isolates (22.0%), blaOXA-539 in 22 isolates (20.1%), and blaOXA-675 in 13 isolates (11.9%). However, 19 (17.4%) isolates carry all blaOXA-145, blaOXA-224, blaOXA-539, and blaOXA-675 genes. The antimicrobial resistance and OXA genes among biofilm former strains were significantly higher than those of nonbiofilm former strains (p < 0.05). The emergence of carbapenem-resistant isolates of P. aeruginosa has posed serious threats to the community because they exhibit multiple drug resistance, thus limiting the therapeutic options for clinicians.
Copyright © 2022 Arash Sezadehghani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of OXA-type Class D β-lactamases Among Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Multiple Centers of Tehran, Iran.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2021;21(4):558-563. doi: 10.2174/1871526520999200917152502. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 32942981
-
Prevalence of carbapenem-hydrolyzing OXA-type β-lactamases among Acinetobacter baumannii in patients with severe urinary tract infection.Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2019 Dec 9;67(1):49-55. doi: 10.1556/030.66.2019.030. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2019. PMID: 31813258
-
blaVIM- and blaOXA-mediated carbapenem resistance among Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from the Mulago hospital intensive care unit in Kampala, Uganda.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Oct 16;19(1):853. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4510-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31619192 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Oxacillinases in Acinetobacter baumannii in Children from Croatia.Chemotherapy. 2019;64(4):167-172. doi: 10.1159/000503746. Epub 2019 Nov 8. Chemotherapy. 2019. PMID: 31707391
-
Incidence and Molecular Characterization of Carbapenemase Genes in Association with Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Tertiary Healthcare Facilities in Southwest Nigeria.Curr Microbiol. 2021 Dec 14;79(1):27. doi: 10.1007/s00284-021-02706-3. Curr Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34905085
Cited by
-
Emergence of NDM-1-producing Raoultella ornithinolytica from reservoir water in Northeast Thailand.Vet World. 2023 Nov;16(11):2321-2328. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2023.2321-2328. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Vet World. 2023. PMID: 38152267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Porbaran M., Tahmasebi H., Arabestani M. A comprehensive study of the relationship between the production of β-lactamase enzymes and iron/siderophore uptake regulatory genes in clinical isolates of acinetobacter baumannii. International Journal of Microbiology . 2021;2021:8. doi: 10.1155/2021/5565537.5565537 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dehbashi S., Tahmasebi H., Zeyni B., Arabestani M. R. Regulation of virulence and β-lactamase gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus isolates: cooperation of two-component systems in bloodstream superbugs. BMC Microbiology . 2021;21(1):192–2021. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02257-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alam M. M., Islam M. N., Hossain Hawlader M. D., et al. Prevalence of multidrug resistance bacterial isolates from infected wound patients in Dhaka, Bangladesh: a cross-sectional study. International Journal of Surgery Open . 2021;28:56–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ijso.2020.12.010. - DOI
-
- Gomathi M. Chengalpattu, Tamil Nadu: Chengalpattu Medical College; 2016. Characterisation and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of non fermenting gram negative bacilli and molecular analysis of Acinetobacter spp., from various clinical samples in a tertiary care hospital. Masters thesis.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

