Radiologically Guided Versus Blinded Intra-articular Injection in Patients With Hip Osteoarthritis: A Retrospective Comparative Study
- PMID: 36032389
- PMCID: PMC9411738
- DOI: 10.1177/11795441221118920
Radiologically Guided Versus Blinded Intra-articular Injection in Patients With Hip Osteoarthritis: A Retrospective Comparative Study
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to present the clinical results of patients with Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) stage 2-4 hip osteoarthritis who were administered intra-articular corticosteroid (CS) or hyaluronic acid (HA), with or without fluoroscopy.
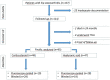
Methods: This retrospective comparative study was conducted in the clinics where the authors worked between 2010 and 2018. Patients with stage 2-4 hip osteoarthritis according to KL criteria were included in the study. Age, body mass index, American Society of Anesthesiologists stages, and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) scores (3rd, 6th, and 12th months) were recorded. Two groups were created as patients who underwent injection with or without fluoroscopy guidance. In group 1, CS (triamnisolone) was administered, and in group 2, sodium hyaluronate 88 mg/4 mL was administered. Obtained parameters were compared.
Results: The WOMAC scores at 3 months of both the CS and HA groups were statistically significantly better than before the application, with the improvement in the CS group found to be significantly better than in the HA group (P = .047). At 6 months, the mean WOMAC scores of the CS and HA groups were better than prior to the application, and there was a statistically significant difference (P < .001). No significant difference was found in either the CS or HA group in the comparison of 12-month WOMAC scores with the baseline scores (P = .744 and P = .054).
Conclusion: In symptomatic hip OA patients, intra-articular administration of CS and HA was seen to be effective at 3 and 6 months after administration. However, the effectiveness was determined to have disappeared within 1 year. Furthermore, in hip OA intra-articular drug applications, it was determined that the blinded technique without radiological guidance performed in the outpatient clinic is as effective and safe as the radiologically guided technique administered in the operating room.
Keywords: Hip osteoarthritis; corticosteroids; fluoroscopy; hyaluronic acid; intra-articular injection.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Hawker GA. Osteoarthritis is a serious disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37:3-6. - PubMed
-
- Zhang W, Doherty M, Arden N, et al.; EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). EULAR evidence based recommendations for the management of hip osteoarthritis: report of a task force of the EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64:669-681. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.028886 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

