Synthesis of silver nanoparticles employing Polyalthia longifolia leaf extract and their in vitro antifungal activity against phytopathogen
- PMID: 36032398
- PMCID: PMC9398913
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101320
Synthesis of silver nanoparticles employing Polyalthia longifolia leaf extract and their in vitro antifungal activity against phytopathogen
Abstract
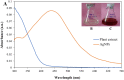
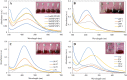
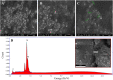
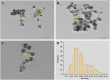
The P. longifolia mediated silver (PL-AgNPs) nanoparticles are very stable and efficient. UV-Vis spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering (DLS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) were used to characterize the produced AgNPs. UV-Vis analysis showed a characteristic peak at 435 nm corresponding to surface plasmon resonance. The synthesis process was spectrophotometrically optimized for various parameters. After optimization, highly stable AgNPs were prepared using 3.0 ml of P. longifolia leaf extract, pH 7.0, 1.0 mM AgNO3, and 60 °C. The zeta potential was measured by DLS, which showed -20.8 mV and the PDI value was 5.42. TEM and SEM analysis shows a spherical shape of the synthesized nanoparticles, and the size was measured between 10 and 40 nm. EDX analysis showed intense peaks from silver and oxygen and small peaks from various metal atoms such as Na, P, S and Al indicating their presence in trace amounts. The average size of the PL-AgNPs was 14 nm. The phytochemical analysis shows that the presence of alkaloids, essential oils and saponins seems to be responsible for the synthesis of nanoparticles. PL-AgNPs were further investigated for their antifungal activity against Alternaria alternata. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) and effect of nanoparticles on cytomorphology of A. alternata have also been reported. Biosynthesized nanoparticles have proven to be inexpensive, environmentally friendly, stable, easily reproducible, and highly effective against plant-pathogenic fungi.
Keywords: Antifungal activity; Cyto-morphology; Green synthesis; Polyalthia longifolia; Silver nanoparticle.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported.
Figures




References
-
- Raj S., Trivedi R., Soni V. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles, characterization and their applications—a review. Surfaces. 2021;5(1):67–90.
-
- Kang S., Herzberg M., Rodrigues D.F., Elimelech M. Antibacterial effects of carbon nanotubes: size does matter. Langmuir. 2008;24(13):6409–6413. - PubMed
-
- Buzea C., Pacheco, Robbie K. Nanomaterials and nanoparticles: sources and toxicity. Biointerphases. 2007;2(4):MR17–71. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

