NMR spectroscopy spotlighting immunogenicity induced by COVID-19 vaccination to mitigate future health concerns
- PMID: 36032416
- PMCID: PMC9393187
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crimmu.2022.08.006
NMR spectroscopy spotlighting immunogenicity induced by COVID-19 vaccination to mitigate future health concerns
Abstract
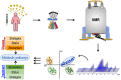
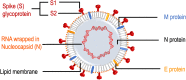
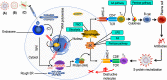
In this review, the disease and immunogenicity affected by COVID-19 vaccination at the metabolic level are described considering the use of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy for the analysis of different biological samples. Consistently, we explain how different biomarkers can be examined in the saliva, blood plasma/serum, bronchoalveolar-lavage fluid (BALF), semen, feces, urine, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and breast milk. For example, the proposed approach for the given samples can allow one to detect molecular biomarkers that can be relevant to disease and/or vaccine interference in a system metabolome. The analysis of the given biomaterials by NMR often produces complex chemical data which can be elucidated by multivariate statistical tools, such as PCA and PLS-DA/OPLS-DA methods. Moreover, this approach may aid to improve strategies that can be helpful in disease control and treatment management in the future.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chemometrics; Immunogenicity; Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy; Vaccination.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
1H NMR To Evaluate the Metabolome of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALf) in Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome (BOS): Toward the Development of a New Approach for Biomarker Identification.J Proteome Res. 2017 Apr 7;16(4):1669-1682. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b01038. Epub 2017 Mar 14. J Proteome Res. 2017. PMID: 28245130
-
Analysis of urinary metabolomic profiling for unstable angina pectoris disease based on nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.Mol Biosyst. 2015 Dec;11(12):3387-96. doi: 10.1039/c5mb00489f. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Mol Biosyst. 2015. PMID: 26471262
-
Study on plasmatic metabolomics of Uygur patients with essential hypertension based on nuclear magnetic resonance technique.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(23):3673-80. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25535139
-
The role of metabolomics in neonatal and pediatric laboratory medicine.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Nov 15;426:127-38. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.08.020. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 24035970 Review.
-
Bioinformatics tools for the analysis of NMR metabolomics studies focused on the identification of clinically relevant biomarkers.Brief Bioinform. 2016 May;17(3):541-52. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbv077. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Brief Bioinform. 2016. PMID: 26342127 Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV2 variants differentially impact on the plasma metabolome.Metabolomics. 2025 Apr 5;21(2):50. doi: 10.1007/s11306-025-02238-y. Metabolomics. 2025. PMID: 40186806 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Mitochondrial DNA Sequencing Using Fecal Samples from Domestic Dogs.Animals (Basel). 2024 Oct 5;14(19):2872. doi: 10.3390/ani14192872. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409821 Free PMC article.
-
NMR-Metabolomics in COVID-19 Research.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1412:197-209. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-28012-2_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37378768
References
-
- Ali S., Badshah G., da Ros Montes D'Oca C., Ramos Campos F., Nagata N., Khan A., de Fátima Costa Santos M., Barison A. High-resolution magic angle spinning (HR-MAS) NMR-based fingerprints determination in the medicinal plant Berberis laurina. Molecules. 2020;25:3647. doi: 10.3390/molecules25163647. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ali S., Rech K.S., Badshah G., Soares F.L.F., Barison A. 1H HR-MAS NMR-based metabolomic fingerprinting to distinguish morphological similarities and metabolic profiles of Maytenus ilicifolia, a Brazilian medicinal plant. J. Nat. Prod. 2021;84:1707–1714. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01094. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

