Pyroptosis in sepsis: Comprehensive analysis of research hotspots and core genes in 2022
- PMID: 36032662
- PMCID: PMC9402944
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.955991
Pyroptosis in sepsis: Comprehensive analysis of research hotspots and core genes in 2022
Abstract
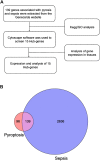
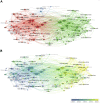
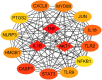
Sepsis, a life-threatening disease caused by dysregulated host response to infection, is a major public health problem with a high mortality and morbidity rate. Pyroptosis is a new type of programmed cell death discovered in recent years, which has been proved to play an important role in sepsis. Nevertheless, there is no comprehensive report, which can help researchers get a quick overview and find research hotspots. Thus, we aimed to identify the study status and knowledge structures of pyroptosis in sepsis and summarize the key mechanism of pyroptosis in sepsis. The data were retrieved and downloaded from the WOS database. Software such as VOSviewer was used to analyze these publications. Key genes were picked out by using (https://www.genecards.org) and (http://www.bioinformatics.com). Then, Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis were used to performed these key genes. From 2011 to 2021, a total of 299 papers met the search criteria, and the global interest in pyroptosis in sepsis measured by the value of (RRI) has started to increase since 2016. China ranked first in the number of publications, followed by the USA. The journal Frontiers in Immunology published the most relevant articles. Through keyword co-occurrence analysis, the high-frequency subject terms were divided into three clusters like "animal research", "cell research," and "molecular research" clusters. "mir," "aki," "monocyte," and "neutrophil" were the newest keywords that may be the hotspot. In addition, a total of 15 genes were identified as hub genes. TNF, IL-1β, AKT1, CASP1, and STAT3 were highly expressed in lung tissues, thymus tissues, and lymphocytes. KEGG analysis indicated that pyroptosis may play a vital role in sepsis via the NOD, PI3K/AKT, and MAPK/JNK pathways. Through the quantitative analysis of the literature on pyroptosis in sepsis, we revealed the current status and hotspots of research in this field and provided some guidance for further studies.
Keywords: NLRP3 and immune organs; bibliometrics; pyroptosis; sepsis; toll and nod signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2022 Xia, Wang, Yao, Han, Zheng, He, Liu and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bibliometric analysis of global research trends on pyroptosis in lung disease.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 13;13:978552. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.978552. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36177039 Free PMC article.
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of Pyroptosis From 2001 to 2021.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 18;12:731933. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.731933. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484243 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular investigation of candidate genes for pyroptosis-induced inflammation in diabetic retinopathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 25;13:918605. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.918605. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35957838 Free PMC article.
-
Bufalin: A Systematic Review of Research Hotspots and Antitumor Mechanisms by Text Mining and Bioinformatics.Am J Chin Med. 2020;48(7):1633-1650. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X20500810. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Am J Chin Med. 2020. PMID: 33148004
-
Publication trends of research on COVID-19 and host immune response: A bibliometric analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 8;10:939053. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.939053. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36003630 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting the prognosis in patients with sepsis by a pyroptosis-related gene signature.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 21;13:1110602. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1110602. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36618365 Free PMC article.
-
Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Ameliorates LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury By Modulating M2a Macrophage Polarization Via the TREM2/PI3K/Akt Pathway.Inflammation. 2023 Dec;46(6):2147-2164. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01868-5. Epub 2023 Aug 11. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 37566293 Free PMC article.
-
Sea dragon metabolome and lipidome unveil bioactive functional food candidates with sepsis therapeutic activities.NPJ Sci Food. 2025 Jun 19;9(1):106. doi: 10.1038/s41538-025-00469-w. NPJ Sci Food. 2025. PMID: 40537493 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoadjuvant therapy in the regulation of cell death in sepsis: recent advances and future directions.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 10;15:1493214. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1493214. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39720718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of the Pathophysiology of Neonatal Stroke and a Critique of Current and Future Therapeutic Strategies.Cells. 2025 Jun 16;14(12):910. doi: 10.3390/cells14120910. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40558537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

