Alternating exosomes and their mimetics as an emergent strategy for targeted cancer therapy
- PMID: 36032679
- PMCID: PMC9399404
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.939050
Alternating exosomes and their mimetics as an emergent strategy for targeted cancer therapy
Abstract
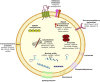
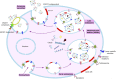
Exosomes, a subtype of the class of extracellular vesicles and nano-sized particles, have a specific membrane structure that makes them an alternative proposition to combat with cancer through slight modification. As constituents of all most all the primary body fluids, exosomes establish the status of intercellular communication. Exosomes have specific proteins/mRNAs and miRNAs which serve as biomarkers, imparting a prognostic tool in clinical and disease pathologies. They have efficient intrinsic targeting potential and efficacy. Engineered exosomes are employed to deliver therapeutic cargos to the targeted tumor cell or the recipient. Exosomes from cancer cells bring about changes in fibroblast via TGFβ/Smad pathway, augmenting the tumor growth. These extracellular vesicles are multidimensional in terms of the functions that they perform. We herein discuss the uptake and biogenesis of exosomes, their role in various facets of cancer studies, cell-to-cell communication and modification for therapeutic and diagnostic use.
Keywords: biomarker; exosome; exosome mimetics; targeted delivery; therapeutics.
Copyright © 2022 Mishra, Pandey, Gupta, Gupta, Sharma and Mishra.
Conflict of interest statement
Author MS was employed by Betterhumans Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials