Left ventricular remodeling and systolic function changes in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a comprehensive contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance study
- PMID: 36033230
- PMCID: PMC9412210
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-22-38
Left ventricular remodeling and systolic function changes in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a comprehensive contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance study
Abstract
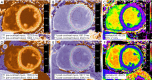
Background: A comprehensive assessment of left ventricular (LV) remodeling and systolic function using contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging in patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) has not yet been reported. This retrospective case-control study aimed to explore and assess the myocardial structure, function, and tissue characteristic changes of LV remodeling in patients with OSA using the CMR method.
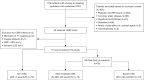
Methods: Fifty-one selected participants 32 OSA and 19 non-OSA underwent overnight polysomnography and CMR examination using T1 mapping and feature tracking techniques. Twenty age- and sex-matched healthy controls were also enrolled for comparison between the groups.
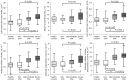
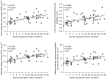
Results: Patients were grouped by apnea-hypopnea index (AHI): AHI <5 events/h as non-OSA group (n=19, 40.7±8.0 years), 5-30 events/h as mild-moderate OSA (n=13, 47.8±9.4 years), and >30 events/h as severe OSA (n=19, 39.0±10.0 years). The OSA group had a higher LV mass index (LVMI) to height2.7 than the non-OSA and healthy control groups (21.0±3.8 vs. 16.4±3.1 and 16.3±3.2 mL/m2.7, P<0.001). Compared with healthy controls, OSA patients had lower global circumferential strain values, although the LV ejection fraction was preserved. Late gadolinium enhancement was not detected in all participants, whereas the extracellular volume fraction was lower in patients with OSA than in the non-OSA and healthy control groups (24.4%±1.9% vs. 26.2%±2.5%, P=0.006 and 24.4%±1.9% vs. 26.5%±2.3%, P=0.004, respectively). The indexed cellular volume (iCV) of the myocardium was significantly higher in subjects with mild-to-moderate and severe OSA than in those without OSA (14.2±2.3 and 15.8±3.1 vs. 11.6±2.4 mL/m2.7, P<0.05). On multivariate linear regression analysis of patients with two different models, OSA severity remained significantly associated with increased LVMI (β=0.348, P=0.004 and β=0.233, P=0.048, respectively) and iCV (β=0.337, P=0.004 and β=0.231, P=0.047, respectively) after adjusting for clinical risk factors.
Conclusions: LVMI is elevated in OSA with a normal LV ejection fraction, mainly with cellular hypertrophy. Cellular hypertrophy without focal fibrosis in OSA may be our main finding.
Keywords: Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR); T1 mapping; feature tracking (FT); obstructive sleep apnea (OSA); ventricular remodeling.
2022 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://cdt.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/cdt-22-38/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
