A Worldwide Survey of Activities and Practices in Clinical Islet of Langerhans Transplantation
- PMID: 36033644
- PMCID: PMC9402897
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2022.10507
A Worldwide Survey of Activities and Practices in Clinical Islet of Langerhans Transplantation
Abstract
A global online survey was administered to 69 islet transplantation programs, covering 84 centers and 5 networks. The survey addressed questions on program organization and activity in the 2000-2020 period, including impact on activity of national health care coverage policies. We obtained full data from 55 institutions or networks worldwide and basic activity data from 6 centers. Additional data were obtained from alternative sources. A total of 94 institutions and 5 networks was identified as having performed islet allotransplantation. 4,365 islet allotransplants (2,608 in Europe, 1,475 in North America, 135 in Asia, 119 in Oceania, 28 in South America) were reported in 2,170 patients in the survey period. From 15 centers active at the start of the study period, the number of simultaneously active islet centers peaked at 54, to progressively decrease to 26 having performed islet allotransplants in 2020. Notably, only 16 centers/networks have done >100 islet allotransplants in the survey period. Types of transplants performed differed notably between North America and the rest of the world, in particular with respect to the near-absence of simultaneous islet-kidney transplantation. Absence of heath care coverage has significantly hampered transplant activity in the past years and the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020.
Keywords: IAK; ITA; SIK; activity; health care coverage; indications; islet transplantation; type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2022 Berney, Andres, Bellin, de Koning, Johnson, Kay, Lundgren, Rickels, Scholz, Stock, White and the International Islet Transplant Centers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
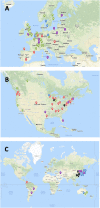
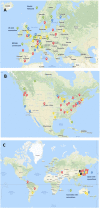

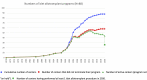
 Cumulative number of centers.
Cumulative number of centers.  Number of centers that did not terminate their program.
Number of centers that did not terminate their program.  Number of active centers (program not “on hold”).
Number of active centers (program not “on hold”).  Number of centers having performed at least 1 islet allotransplant procedure in 2020.
Number of centers having performed at least 1 islet allotransplant procedure in 2020.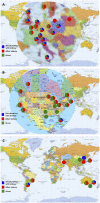
References
-
- International Islet Transplant Registry (ITR). Newsletter (2001). Available from: https://www.med.uni-giessen.de/itr/newsletter/no_9/news_9.pdf.
-
- Collaborative Islet Transplant Registry (CITR). Tenth Annual Report (2017). Available from: https://citregistry.org/system/files/10th_AR.pdf.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

