Antiproliferative Potential of Gloriosine: A Lead for Anticancer Drug Development
- PMID: 36033689
- PMCID: PMC9404168
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02688
Antiproliferative Potential of Gloriosine: A Lead for Anticancer Drug Development
Abstract
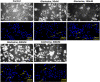
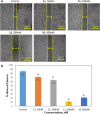
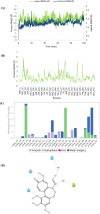
Gloriosine, a colchicine-like natural product, is widely obtained from Gloriosa superba roots. Despite having remarkable anticancer potential, colchicine could not pave its way to the clinic, while gloriosine is yet to be investigated for its pharmacological effects. In the present work, 14 compounds, including gloriosine, were isolated from the G. superba roots and were characterized by NMR spectroscopy. Gloriosine (11) was evaluated for its antiproliferative activity against a panel of 15 human cancer cell lines of different tissues and normal breast cells. Gloroisine (11) displayed significant antiproliferative activity against various cancer cell lines selectively, with IC50 values ranging from 32.61 to 100.28 nM. Further, gloriosine (11) was investigated for its apoptosis-inducing ability and found to form apoptotic bodies. It also inhibited A549 cell migration in the wound healing assay. Finally, molecular docking studies were performed to explore the possible binding modes of gloriosine with the colchicine-binding site of tubulin protein. Our findings suggested that gloriosine might be a potential lead for anticancer drug discovery.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Verma S.; Eikelboom J. W.; Nidorf S. M.; Al-Omran M.; Gupta N.; Teoh H.; Friedrich J. O. Colchicine in cardiac disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2015, 15, 96 10.1186/s12872-015-0068-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Deftereos S.; Giannopoulos G.; Papoutsidakis N.; Panagopoulou V.; Kossyvakis C.; Raisakis K.; Cleman M. W.; Stefanadis C. Colchicine and the Heart: Pushing the Envelope. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1817–1825. 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.08.726. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hagras M.; El Deeb M. A.; Elzahabi H. S. A.; Elkaeed E. B.; Mehany A. B. M.; Eissa I. H. Discovery of new quinolines as potent colchicine binding site inhibitors: design, synthesis, docking studies, and anti-proliferative evaluation. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 640–658. 10.1080/14756366.2021.1883598. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eissa I. H.; Dahab M. A.; Ibrahim M. K.; Alsaif N. A.; Alanazi A. Z.; Eissa S. I.; Mehany A. B. M.; Beauchemin A. M. Design and discovery of new antiproliferative 1,2,4-triazin-3(2H)-ones as tubulin polymerization inhibitors targeting colchicine binding site. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 112, 104965 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104965. - DOI - PubMed
- El-Naggar A. M.; Eissa I. H.; Belal A.; El-Sayed A. A. Design, eco-friendly synthesis, molecular modeling and anticancer evaluation of thiazol-5(4H)-ones as potential tubulin polymerization inhibitors targeting the colchicine binding site. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 2791–2811. 10.1039/C9RA10094F. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

