Obamacare: A bibliometric perspective
- PMID: 36033824
- PMCID: PMC9416003
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.979064
Obamacare: A bibliometric perspective
Abstract
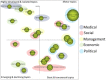
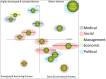
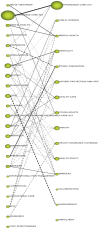
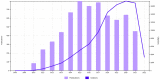
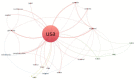
Obamacare is the colloquial name given to the Affordable Care Act (ACA) signed into law by President Obama in the USA, which ultimately aims to provide universal access to health care services for US citizens. The aim of this paper is to provide an overview of the political-legal, economic, social, management (or administrative), and medical (or health) repercussions of this law, using a bibliometric methodology as a basis. In addition, the main contributors to research on ACA issues have been identified in terms of authors, organizations, journals, and countries. The downward trend in scientific production on this law has been noted, and it has been concluded that a balance has not yet been reached between the coexistence of private and public health care that guarantees broad social coverage without economic or other types of barriers. The law requires political consensus to be implemented in a definitive and global manner for the whole of the United States.
Keywords: Affordable Care Act; Obamacare; PEST analysis; SciMAT; strategic diagram.
Copyright © 2022 Carrasco-Aguilar, Galán and Carrasco.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Critical Analysis of Obamacare: Affordable Care or Insurance for Many and Coverage for Few?Pain Physician. 2017 Mar;20(3):111-138. Pain Physician. 2017. PMID: 28339427 Review.
-
Evolution of US Health Care Reform.Pain Physician. 2017 Mar;20(3):107-110. Pain Physician. 2017. PMID: 28339426 Review.
-
Obamacare 2012: prognosis unclear for interventional pain management.Pain Physician. 2012 Sep-Oct;15(5):E629-40. Pain Physician. 2012. PMID: 22996858 Review.
-
Repeal and Replace of Affordable Care: A Complex, but Not an Impossible Task.Pain Physician. 2016 Nov-Dec;19(8):E1109-E1113. Pain Physician. 2016. PMID: 27906931
-
Why do so many Americans oppose the Affordable Care Act?Am J Med. 2015 Aug;128(8):807-10. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.01.032. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Am J Med. 2015. PMID: 25731135
Cited by
-
Healthcare Systems across Europe and the US: The Managed Entry Agreements Experience.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Feb 3;11(3):447. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11030447. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36767022 Free PMC article.
-
Data Sources as a Driver for Market-Oriented Tourism Organizations: a Bibliometric Perspective.J Knowl Econ. 2023 May 25:1-34. doi: 10.1007/s13132-023-01334-5. Online ahead of print. J Knowl Econ. 2023. PMID: 40479121 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Finegold K, Conmy A, Chu RC, Bosworth A, Sommers BD. Trends in the US Uninsured Population. Washington, DC: Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation; (2021).
-
- Arrieta A. Seguro de salud y principio contributivo de la seguridad social en los Estados Unidos de América. Revista latinoamericana de derecho social. (2016) 23:3–30. 10.1016/j.rlds.2016.08.001 - DOI
-
- Salinas AG. ¿Qué es el ≪Obamacare≫? Dendra Médica. Revista de Humanidades. (2013) 12:320–9.
-
- Montaña AN. Análisis de la evolución y delimitación de los estudios métricos cuantitativos bibliometría, cienciometría e infometría. (2021). Available online at: http://hdl.handle.net/10554/58609 (accessed November 26, 2021).
-
- Cobo MJ, López-Herrera AG, Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F. SciMAT: a new science mapping analysis software tool. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol. (2012) 63:1609–30. 10.1002/asi.22688 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

