Building Programs to Eradicate Toxoplasmosis Part I: Introduction and Overview
- PMID: 36034212
- PMCID: PMC9395898
- DOI: 10.1007/s40124-022-00269-w
Building Programs to Eradicate Toxoplasmosis Part I: Introduction and Overview
Abstract
Purpose of review: Review building of programs to eliminate Toxoplasma infections.
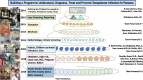
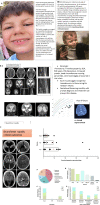
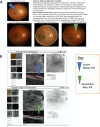
Recent findings: Morbidity and mortality from toxoplasmosis led to programs in USA, Panama, and Colombia to facilitate understanding, treatment, prevention, and regional resources, incorporating student work.
Summary: Studies foundational for building recent, regional approaches/programs are reviewed. Introduction provides an overview/review of programs in Panamá, the United States, and other countries. High prevalence/risk of exposure led to laws mandating testing in gestation, reporting, and development of broad-based teaching materials about Toxoplasma. These were tested for efficacy as learning tools for high-school students, pregnant women, medical students, physicians, scientists, public health officials and general public. Digitized, free, smart phone application effectively taught pregnant women about toxoplasmosis prevention. Perinatal infection care programs, identifying true regional risk factors, and point-of-care gestational screening facilitate prevention and care. When implemented fully across all demographics, such programs present opportunities to save lives, sight, and cognition with considerable spillover benefits for individuals and societies.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s40124-022-00269-w.
Keywords: Brazil; Colombia; France; Morocco; Panama; United States; congenital toxoplasmosis; foundational work; medical care; public health; pyrimethamine; review; student research; sulfadiazine; toxoplasmosis.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestDenis Limonne Pharm D, PhD and Raphael Piarroux Pharm D, PhD, are the owner and Scientists at LDBio. A patent application was submitted in the United States for the development of the whole blood point of care test with the scientists at the University of Chicago to insure its continued high-quality performance and reproducibility of the results described herein. In the United States and Panama in the more recent studies the LDBio kit was provided for the studies without charge by D Limonne. The Roche kit was provided without charge in Panama. For the predicate test costs for the comparison test for 70 consecutive persons for the feasibility clinical trial the cost of performing the Biorad IgG and IgM tests was provided by Kiphard Foundation. Kamal El Bissati is heading the initiatives to prevent toxoplasmosis in Morocco. Patents have been obtained for the medicine, anti-sense, vaccine, biomarker development work to facilitate their development toward clinical use and sustain availability if/when they are used in clinical practice. RMcLeod was reimbursed for time in performing a literature review concerning Spiramycin by Sanofi Pasteur in accordance with Sunshine laws. RMcLeod (with her colleagues) shared first prize merit award in the Alzgerm initiative to identify the highest quality and rigorously developed and described work demonstrating that a pathogen can initiate, progress and contribute to neurodegenerative diseases, and that there can be effect of this chronic active infection on cognition, motor function and other disease processes. This monetary prize was used to further this ongoing work.Competing InterestsThere are no other disclosures and no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Mcleod R, Mack DG, Boyer K, Mets M, Roizen N, Swisher C, Patel D, Beckmann E, Vitullo D, Johnson D, et al. Phenotypes and functions of lymphocytes in congenital toxoplasmosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1990;116(5):623–635. - PubMed
-
- McGee T, Wolters C, Stein L, Kraus N, Johnson D, Boyer K, Mets M, Roizen N, Beckman J, Meier P, Swisher C, Holfels E, Withers S, McLeod R. Absence of sensorineural hearing loss in treated infants and children with congenital toxoplasmosis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992;106(1):75–80. doi: 10.1177/019459989210600131. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mcleod R, Mack D, Foss R, Boyer K, Withers S, Levin S, Hubbell J. Levels of pyrimethamine in sera and cerebrospinal and ventricular fluids from infants treated for congenital toxoplasmosis. Toxoplasmosis Study Group. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992;36(5):1040–1048. doi: 10.1128/AAC.36.5.1040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McAuley J, Boyer KM, Patel D, Mets M, Swisher C, Roizen N, Wolters C, Stein L, Stein M, Schey W, Remington J, Meier P, Johnson D, Heydemann P, Holfels E, Withers S, Mack D, Brown C, Patton D, McLeod R. Early and longitudinal evaluations of treated infants and children and untreated historical patients with congenital toxoplasmosis: the Chicago Collaborative Treatment Trial. Clin Infect Dis. 1994;18(1):38–72. doi: 10.1093/clinids/18.1.38. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Swisher CN, Boyer K, McLeod R. Congenital toxoplasmosis. In JB Bodensteiner, Ed. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 1994;1:4–25. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
