Improved Quantification by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of the Fatty Acid Ester Composition of Extra Virgin Olive Oils
- PMID: 36034339
- PMCID: PMC9396653
- DOI: 10.1021/acsfoodscitech.2c00057
Improved Quantification by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of the Fatty Acid Ester Composition of Extra Virgin Olive Oils
Abstract
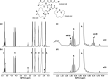
Analysis of foods, which are typically highly complex mixtures, by 1H NMR can be difficult because the prevalence of signal overlap complicates characterization and quantification. The various components of a food sample may have a wide range of concentrations, leading to a high dynamic range NMR spectrum and complicating the analysis of less concentrated species. One source of this complication is the presence of 13C satellites, peaks that appear either side of a parent peak with ∼0.56% of its intensity. Satellites of concentrated species can easily be comparable in intensity to the signals of minor components, and can partly or wholly obscure them. This is commonly seen in olive oil samples, leading to inaccurate calculation of the fatty acid ester composition of the oil, used for determining the quality of edible oils and for detecting adulteration. Here, we show that the recently introduced Destruction of Interfering Satellites by Perfect Echo Low-pass filtration (DISPEL) experiment is able to suppress 13C satellites and can substantially improve the accuracy of integration of minor signals. The DISPEL experiment does not require any complicated optimization, working "out of the box" with standard parameters, and incurs no significant loss of sensitivity. It has the potential to become the default experiment, replacing conventional 1D 1H NMR, for quantitative analysis of olive oil.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Servili M.; Baldioli M.; Selvaggini R.; Miniati E.; Macchioni A.; Montedoro G. High-Perfromance Liquid Chromatography Evaluation of Phenols in Olive Fruit, Virgin Olive Oil, Vegetation Waters, and Pomace and 1D- and 2D-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Characterisation. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 873–882. 10.1007/s11746-999-0079-2. - DOI
-
- Karkoula E.; Skantzari A.; Melliou E.; Magiatis P. Direct measurement of oleocanthal and oleacein levels in olive oil by quantitative 1H NMR. Establishment of a new index for the characterization of extra virgin olive oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11696–11703. 10.1021/jf3032765. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gorzynik-Debicka M.; Przychodzen P.; Cappello F.; Kuban-Jankowska A.; Marino Gammazza A.; Knap N.; Wozniak M.; Gorska-Ponikowska M. Potential Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Plant Polyphenols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 686.10.3390/ijms19030686. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Romani A.; Ieri F.; Urciuoli S.; Noce A.; Marrone G.; Nediani C.; Bernini R. Health Effects of Phenolic Compounds Found in Extra-Virgin Olive Oil, By-Products, and Leaf of Olea europaea L. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1776.10.3390/nu11081776. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Nocella C.; Cammisotto V.; Fianchini L.; D’Amico A.; Novo M.; Castellani V.; Stefanini L.; Violi F.; Carnevale R. Extra Virgin Olive Oil and Cardiovascular Diseases: Benefits for Human Health. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2018, 18, 4–13. 10.2174/1871530317666171114121533. - DOI - PubMed
- Covas M. I.; Nyyssonen K.; Poulsen H. E.; Kaikkonen J.; Zunft H. J.; Kiesewetter H.; Gaddi A.; de la Torre R.; Mursu J.; Baumler H.; et al. The effect of polyphenols in olive oil on heart disease risk factors: a randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 145, 333–341. 10.7326/0003-4819-145-5-200609050-00006. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
