Crocin-I Protects Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity via Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Inflammation in Mice
- PMID: 36034852
- PMCID: PMC9403484
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.894089
Crocin-I Protects Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity via Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Inflammation in Mice
Abstract
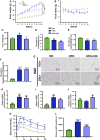
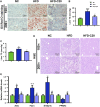
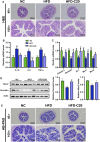
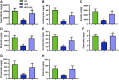
Crocin-I can regulate physiological changes in the human body by altering inflammation and microbial composition. Gut microbiota are also involved in modulating the pathophysiology of obesity. However, crocin-I's effect on obesity and the mechanism underlying its effects on gut microbiota and inflammation remain poorly understood. Here, high-fat diet (HFD) -induced obese mice were administrated crocin-I (20 mg/kg/day) for 10 weeks using an oral gavage (HFD-C20 group). HFD-C20, HFD, and Normal chow (NC) groups were compared. The fat content, colon tissue inflammatory cytokine levels, gut microbiota, and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) levels were measured. We show that crocin-I reduced body weight and liver weight and improved glucose resistance in HFD-induced mice, and reduced the lipid accumulation in the liver. Strikingly, crocin-I alleviated intestinal microbial disorders and decreased the F/B ratio and the abundance of Proteobacteria in HFD-induced obese mice. Crocin-I also rescued the decrease in the levels of SCFAs and repaired altered intestinal barrier functioning and intestinal inflammation in HFD-induced obese mice. These findings indicate that crocin-I may inhibit obesity by modulating the composition of gut microbiota and intestinal inflammation.
Keywords: crocin-i; gut microbiota; inflammation; lipid metabolism; obesity.
Copyright © 2022 Xie, Zhang, Sun, Wang, Zhu, Shu, Wu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Boscaini S., Cabrera-Rubio R., Golubeva A., Nychyk O., Fülling C., Speakman J. R., et al. (2021). Depletion of the Gut Microbiota Differentially Affects the Impact of Whey Protein on High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Intestinal Permeability. Physiol. Rep. 9, e14867. 10.14814/phy2.14867 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

