Metabolomics approach reveals high energy diet improves the quality and enhances the flavor of black Tibetan sheep meat by altering the composition of rumen microbiota
- PMID: 36034898
- PMCID: PMC9405419
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.915558
Metabolomics approach reveals high energy diet improves the quality and enhances the flavor of black Tibetan sheep meat by altering the composition of rumen microbiota
Abstract
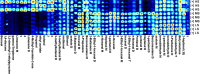
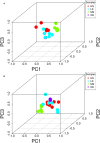
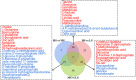
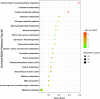
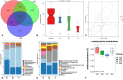
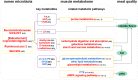
This study aims to determine the impact of dietary energy levels on rumen microbial composition and its relationship to the quality of Black Tibetan sheep meat by applying metabolomics and Pearson's correlation analyses. For this purpose, UHPLC-QTOF-MS was used to identify the metabolome, whereas 16S rDNA sequencing was used to detect the rumen microbiota. Eventually, we observed that the high energy diet group (HS) improved the carcass quality of Black Tibetan sheep and fat deposition in the longissimus lumborum (LL) compared to the medium energy diet group (MS). However, HS considerably increased the texture, water holding capacity (WHC), and volatile flavor of the LL when compared to that of MS and the low energy diet group (LS). Metabolomics and correlation analyses revealed that dietary energy levels mainly affected the metabolism of carbohydrates and lipids of the LL, which consequently influenced the content of volatile flavor compounds (VOCs) and fats. Furthermore, HS increased the abundance of Quinella, Ruminococcus 2, (Eubacterium) coprostanoligenes, and Succinivibrionaceae UCG-001, all of which participate in the carbohydrate metabolism in rumen and thus influence the metabolite levels (stachyose, isomaltose, etc.) in the LL. Overall, a high-energy diet is desirable for the production of Black Tibetan sheep mutton because it improves the mouthfeel and flavor of meat by altering the composition of rumen microbiota, which influences the metabolism in the LL.
Keywords: black Tibetan sheep; dietary energy levels; meat quality; metabolomics; rumen microbiota.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Han, Hou, Raza, Gui, Sun, Wang, Yang, Yuan, Simal-Gandara, El-Shehawi, Alswat, Alenezi, Shukry, Sayed and Aloufi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Papi N, Mostafa-Tehrani A, Amanlou H, Memarian M. Effects of dietary forage-to-concentrate ratios on performance and carcass characteristics of growing fat-tailed lambs. Anim Feed Sci Technol. (2011) 163:93–8. 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2010.10.010 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

