Lot verification practices in Ontario clinical chemistry laboratories - Results of a patterns-of-practice survey
- PMID: 36035320
- PMCID: PMC9399155
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plabm.2022.e00300
Lot verification practices in Ontario clinical chemistry laboratories - Results of a patterns-of-practice survey
Abstract
Objectives: Verifying new reagent or calibrator lots is crucial for maintaining consistent test performance. The Institute for Quality Management in Healthcare (IQMH) conducted a patterns-of-practice survey and follow-up case study to collect information on lot verification practices in Ontario.
Methods: The survey had 17 multiple-choice questions and was distributed to 183 licensed laboratories. Participants provided information on materials used and approval/rejection criteria for their lot verification procedures for eight classes of testing systems. The case study provided a set of lot comparison data and was distributed to 132 laboratories. Responses were reviewed by IQMH scientific committees.
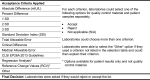
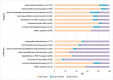
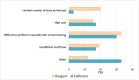
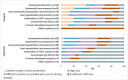
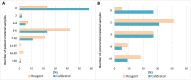
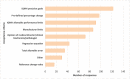
Results: Of the 175 laboratories that responded regarding reagent lot verifications, 74% verified all tests, 11% some, and 15% none. Of the 171 laboratories that responded regarding calibrator lot verifications, 39% verified all calibrators, 4% some, and 57% none. Reasons for not performing verifications ranged from difficulty performing parallel testing to high reagent cost. For automated chemistry assays and immunoassays, 23% of laboratories did not include patient-derived materials in reagent lot verifications and 42% included five to six patient materials; 58% of laboratories did not include patient-derived materials in calibrator lot verifications and 23% included five to six patient materials. Different combinations of test-specific rules were used for acceptance criteria. For a failed lot, 98% of laboratories would investigate further and take corrective actions. Forty-three percent of laboratories would accept the new reagent lot in the case study.
Conclusion: Responses to the survey and case study demonstrated variability in lot verification practices among laboratories.
Keywords: CLSI, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; Calibrator; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; GC, gas chromatography; HPLC, high-performance liquid chromatography; IQMH, Institute for Quality Management in Healthcare; ISO, International Organization for Standardization; LC-MS/MS, liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry; Lot number; PT, proficiency testing; QC, quality control; RIA, radioimmunoassay; Reagent; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone; Verification.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
-
- Algeciras-Schimnich A. “Tackling reagent lot-to-lot verification in the clinical laboratory.” AACC.org. https://www.aacc.org/cln/articles/2014/july/bench-matters Accessed.
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute . Approved Guideline. CLSI Document EP26-A; 2013. User Evaluation of Between-Reagent Lot Variation.
-
- International Organization for Standardization . third ed. 2012. ISO 15189 Medical Laboratories – Requirements for Quality and Competence.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

