Comprehensive Analysis of Transcriptional Expression of hsa-mir-21 Predicted Target Genes and Immune Characteristics in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 36035369
- PMCID: PMC9413563
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.73404
Comprehensive Analysis of Transcriptional Expression of hsa-mir-21 Predicted Target Genes and Immune Characteristics in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
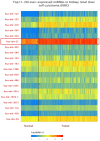
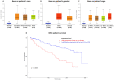
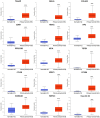
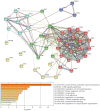
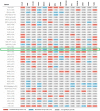
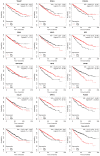
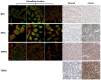
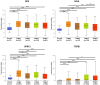
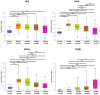
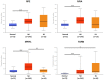
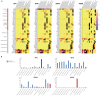
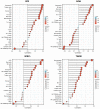
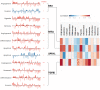
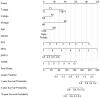
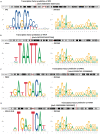
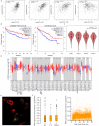
Background: To uncover advanced prognosis biomarkers in patient with kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC), our study was the first to make a comprehensive analysis of hsa-mir-21 predicted target genes and explore the immune characteristics in KIRC. Methods: In this study, the comprehensive analysis of hsa-mir-21 predicted target genes and immune characteristics in KIRC were analyzed via TIMER2.0, UALCAN, Metascape, Kaplan-Meier plotter, Human Protein Atlas, CancerSEA, JASPAR, GEPIA, R package: GSVA package (version 1.34.0) & immune infiltration algorithm (ssGSEA) and R package: RMS package (version 6.2-0) & SURVIVAL package (version 3.2-10). Results: Up-transcriptional expressions of RP2, NFIA, SPRY1 were significantly associated with favorable prognosis in KIRC, whereas that of TGFBI was markedly significantly to unfavorable prognosis. Additionally, RP2, NFIA, SPRY1 and TGFBI were significantly relevant to the immune infiltration in KIRC. Finally, ZNF263 was a common predicted transcription factor of RP2, NFIA, SPRY1 and TGFBI, which can as an independent indicator for prognosis in KIRC patients. Conclusions: Hsa-mir-21 predicted target genes (RP2, NFIA, SPRY1 and TGFBI) and the common transcription factor ZNF263 could be the advanced prognosis biomarkers in KIRC patients.
Keywords: Hsa-mir-21; Immune Characteristics; Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma; Predicted Target Gene; Prediction Model; Prognosis; Transcription Factor.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ZEB family is a prognostic biomarker and correlates with anoikis and immune infiltration in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Jun 5;17(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01895-7. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38840097 Free PMC article.
-
LPAR2 correlated with different prognosis and immune cell infiltration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Hereditas. 2022 Mar 4;159(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s41065-022-00229-w. Hereditas. 2022. PMID: 35241179 Free PMC article.
-
A microRNA-clinical prognosis model to predict the overall survival for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2021 Sep;10(17):6128-6139. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4148. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34288551 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA related prognosis biomarkers from high throughput sequencing data of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.BMC Med Genomics. 2021 Mar 9;14(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-00932-z. BMC Med Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33750388 Free PMC article.
-
The combination of NDUFS1 with CD4+ T cell infiltration predicts favorable prognosis in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jul 4;11:1168462. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1168462. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37469574 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of biomarkers for knee osteoarthritis through clinical data and machine learning models.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 11;15(1):1703. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85945-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39799234 Free PMC article.
-
Identified RP2 as a prognostic biomarker for glioma, facilitating glioma pathogenesis mainly via regulating tumor immunity.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Aug 18;15(16):8155-8184. doi: 10.18632/aging.204962. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37602882 Free PMC article.
-
Potential mechanisms and drug prediction of Rheumatoid Arthritis and primary Sjögren's Syndrome: A public databases-based study.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 15;19(2):e0298447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298447. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38359008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen HT, McGovern FJ. Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(23):2477–2490. - PubMed
-
- Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B. Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet. 2009;373(9669):1119–1132. - PubMed
-
- D'Avella C, Abbosh P, Pal SK, Geynisman DM. Mutations in renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol. 2020;38(10):763–773. - PubMed
-
- Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, Reuter VE, Ulbright TM. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur Urol. 2016;70(1):93–105. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

