The role of kidney biopsy in immune checkpoint inhibitor nephrotoxicity
- PMID: 36035427
- PMCID: PMC9399765
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.964335
The role of kidney biopsy in immune checkpoint inhibitor nephrotoxicity
Abstract
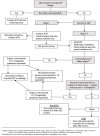
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, medications that boost host immune response to tumor cells, are now at the forefront of anti-cancer therapy. While efficacious in the treatment of patients with advanced cancer, immune checkpoint inhibitors can lead to serious autoimmune side effects involving any organ in the body. Immune checkpoint inhibitor nephrotoxicity is an increasingly recognized cause of acute kidney injury in patients with cancer. This review discusses the clinical and histopathologic diagnosis of immune checkpoint inhibitor nephrotoxicity, highlighting the need for more reliable non-invasive diagnostic testing. We focus on the controversy surrounding the role of kidney biopsy in diagnosis and management of suspected immune checkpoint inhibitor toxicity with inclination toward pursuing kidney biopsy in certain outlined circumstances. Finally, we briefly discuss treatment of immune checkpoint inhibitor nephrotoxicity and the decision to re-challenge immunotherapy in patients who experience these adverse events.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; drug induced kidney injury; immune checkpoint inhibitor; interstitial nephritis; kidney biopsy.
Copyright © 2022 Moss and Perazella.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Strome SE, Dong H, Tamura H, Voss SG, Flies DB, Tamada K, et al. . B7-H1 blockade augments adoptive T-cell immunotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. (2003) 63:6501–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources