Regulation of plant biotic interactions and abiotic stress responses by inositol polyphosphates
- PMID: 36035672
- PMCID: PMC9403785
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.944515
Regulation of plant biotic interactions and abiotic stress responses by inositol polyphosphates
Abstract
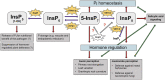
Inositol pyrophosphates (PP-InsPs), derivatives of inositol hexakisphosphate (phytic acid, InsP6) or lower inositol polyphosphates, are energy-rich signaling molecules that have critical regulatory functions in eukaryotes. In plants, the biosynthesis and the cellular targets of these messengers are not fully understood. This is because, in part, plants do not possess canonical InsP6 kinases and are able to synthesize PP-InsP isomers that appear to be absent in yeast or mammalian cells. This review will shed light on recent discoveries in the biosynthesis of these enigmatic messengers and on how they regulate important physiological processes in response to abiotic and biotic stresses in plants.
Keywords: auxin response; inositol pyrophosphate; jasmonic acid signaling pathway; phosphate homeostasis; plant biotic and abiotic stress responses; salicylic acid signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2022 Riemer, Pullagurla, Yadav, Rana, Jessen, Kamleitner, Schaaf and Laha.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Adepoju O., Williams S. P., Craige B., Cridland C. A., Sharpe A. K., Brown A. M., et al. (2019). Inositol trisphosphate kinase and diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate kinase enzymes constitute the inositol pyrophosphate synthesis pathway in plants. bioRxiv [Preprint] 10.1101/724914 - DOI
-
- Adie B., Rubio-Somoza I., Solano R. (2007). Modulation of plant defenses by ethylene. J. Plant Growth Regul. 26 160–177. 10.1007/s00344-007-0012-6 - DOI
-
- Alimohammadi M., de Silva K., Ballu C., Ali N., Khodakovskaya M. V. (2012). Reduction of inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate affects the overall phosphoinositol pathway and leads to modifications in light signalling and secondary metabolism in tomato plants. J. Exp. Bot. 63 825–835. 10.1093/jxb/err306 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen G. J., Sanders D. (1994). Osmotic stress enhances the competence of Beta vulgaris vacuoles to respond to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Plant J. 6 687–695. 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1994.6050687.x - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

