On the Design of Secured and Reliable Dynamic Access Control Scheme of Patient E-Healthcare Records in Cloud Environment
- PMID: 36035822
- PMCID: PMC9410930
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3804553
On the Design of Secured and Reliable Dynamic Access Control Scheme of Patient E-Healthcare Records in Cloud Environment
Retraction in
-
Retracted: On the Design of Secured and Reliable Dynamic Access Control Scheme of Patient E-Healthcare Records in Cloud Environment.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Aug 9;2023:9878602. doi: 10.1155/2023/9878602. eCollection 2023. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37600254 Free PMC article.
Abstract
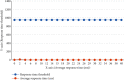
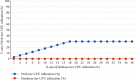
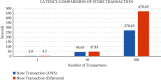
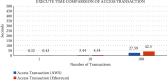
Traditional healthcare services have changed into modern ones in which doctors can diagnose patients from a distance. All stakeholders, including patients, ward boy, life insurance agents, physicians, and others, have easy access to patients' medical records due to cloud computing. The cloud's services are very cost-effective and scalable, and provide various mobile access options for a patient's electronic health records (EHRs). EHR privacy and security are critical concerns despite the many benefits of the cloud. Patient health information is extremely sensitive and important, and sending it over an unencrypted wireless media raises a number of security hazards. This study suggests an innovative and secure access system for cloud-based electronic healthcare services storing patient health records in a third-party cloud service provider. The research considers the remote healthcare requirements for maintaining patient information integrity, confidentiality, and security. There will be fewer attacks on e-healthcare records now that stakeholders will have a safe interface and data on the cloud will not be accessible to them. End-to-end encryption is ensured by using multiple keys generated by the key conclusion function (KCF), and access to cloud services is granted based on a person's identity and the relationship between the parties involved, which protects their personal information that is the methodology used in the proposed scheme. The proposed scheme is best suited for cloud-based e-healthcare services because of its simplicity and robustness. Using different Amazon EC2 hosting options, we examine how well our cloud-based web application service works when the number of requests linearly increases. The performance of our web application service that runs in the cloud is based on how many requests it can handle per second while keeping its response time constant. The proposed secure access scheme for cloud-based web applications was compared to the Ethereum blockchain platform, which uses internet of things (IoT) devices in terms of execution time, throughput, and latency.
Copyright © 2022 Kirtirajsinh Zala et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
















References
-
- Deepa N., Pham Q.-V., Nguyen D. C., et al. A survey on blockchain for big data: approaches,opportunities,and future directions. Future Generation Computer Systems . 2022;131:209–226. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2022.01.017. - DOI
-
- Thakkar H. K., Sahoo P. K., Mohanty P. Dofm: domain feature miner for robust extractive summarization. Information Processing & Management . 2021;58(3) doi: 10.1016/j.ipm.2020.102474.102474 - DOI
-
- Kumar R., Swarnkar M., Singal G., Kumar N. Iot network traffic classification using machine learning algorithms: an experimental analysis. IEEE Internet of Things Journal . 2021;9(2):989–1008. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3121517. - DOI
-
- Mubashar A., Asghar K., Javed A. R., et al. Storage and proximity management for centralized personal health records using an ipfs-based optimization algorithm. Journal of Circuits, Systems, and Computers . 2022;31(01) doi: 10.1142/s0218126622500104.2250010 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

