Effects of Plyometric Jump Training on Measures of Physical Fitness and Sport-Specific Performance of Water Sports Athletes: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis
- PMID: 36036301
- PMCID: PMC9424421
- DOI: 10.1186/s40798-022-00502-2
Effects of Plyometric Jump Training on Measures of Physical Fitness and Sport-Specific Performance of Water Sports Athletes: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: A growing body of literature is available regarding the effects of plyometric jump training (PJT) on measures of physical fitness (PF) and sport-specific performance (SSP) in-water sports athletes (WSA, i.e. those competing in sports that are practiced on [e.g. rowing] or in [e.g. swimming; water polo] water). Indeed, incoherent findings have been observed across individual studies making it difficult to provide the scientific community and coaches with consistent evidence. As such, a comprehensive systematic literature search should be conducted to clarify the existent evidence, identify the major gaps in the literature, and offer recommendations for future studies.
Aim: To examine the effects of PJT compared with active/specific-active controls on the PF (one-repetition maximum back squat strength, squat jump height, countermovement jump height, horizontal jump distance, body mass, fat mass, thigh girth) and SSP (in-water vertical jump, in-water agility, time trial) outcomes in WSA, through a systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized and non-randomized controlled studies.
Methods: The electronic databases PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science were searched up to January 2022. According to the PICOS approach, the eligibility criteria were: (population) healthy WSA; (intervention) PJT interventions involving unilateral and/or bilateral jumps, and a minimal duration of ≥ 3 weeks; (comparator) active (i.e. standard sports training) or specific-active (i.e. alternative training intervention) control group(s); (outcome) at least one measure of PF (e.g. jump height) and/or SSP (e.g. time trial) before and after training; and (study design) multi-groups randomized and non-randomized controlled trials. The Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) scale was used to assess the methodological quality of the included studies. The DerSimonian and Laird random-effects model was used to compute the meta-analyses, reporting effect sizes (ES, i.e. Hedges' g) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs). Statistical significance was set at p ≤ 0.05. Certainty or confidence in the body of evidence for each outcome was assessed using Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE), considering its five dimensions: risk of bias in studies, indirectness, inconsistency, imprecision, and risk of publication bias.
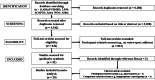
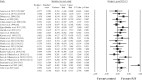
Results: A total of 11,028 studies were identified with 26 considered eligible for inclusion. The median PEDro score across the included studies was 5.5 (moderate-to-high methodological quality). The included studies involved a total of 618 WSA of both sexes (330 participants in the intervention groups [31 groups] and 288 participants in the control groups [26 groups]), aged between 10 and 26 years, and from different sports disciplines such as swimming, triathlon, rowing, artistic swimming, and water polo. The duration of the training programmes in the intervention and control groups ranged from 4 to 36 weeks. The results of the meta-analysis indicated no effects of PJT compared to control conditions (including specific-active controls) for in-water vertical jump or agility (ES = - 0.15 to 0.03; p = 0.477 to 0.899), or for body mass, fat mass, and thigh girth (ES = 0.06 to 0.15; p = 0.452 to 0.841). In terms of measures of PF, moderate-to-large effects were noted in favour of the PJT groups compared to the control groups (including specific-active control groups) for one-repetition maximum back squat strength, horizontal jump distance, squat jump height, and countermovement jump height (ES = 0.67 to 1.47; p = 0.041 to < 0.001), in addition to a small effect noted in favour of the PJT for SSP time-trial speed (ES = 0.42; p = 0.005). Certainty of evidence across the included studies varied from very low-to-moderate.
Conclusions: PJT is more effective to improve measures of PF and SSP in WSA compared to control conditions involving traditional sport-specific training as well as alternative training interventions (e.g. resistance training). It is worth noting that the present findings are derived from 26 studies of moderate-to-high methodological quality, low-to-moderate impact of heterogeneity, and very low-to-moderate certainty of evidence based on GRADE. Trial registration The protocol for this systematic review with meta-analysis was published in the Open Science platform (OSF) on January 23, 2022, under the registration doi https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/NWHS3 (internet archive link: https://archive.org/details/osf-registrations-nwhs3-v1 ).
Keywords: Human physical conditioning; Movement; Muscle strength; Musculoskeletal and neural physiological phenomena; Plyometric exercise; Resistance training.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Rodrigo Ramirez-Campillo, Alejandro Perez-Castilla, Rohit K. Thapa, José Afonso, Filipe Manuel Clemente, Juan C. Colado, Eduardo Saéz de Villarreal and Helmi Chaabene declare that they have no conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this review.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Plyometric-Jump Training Effects on Physical Fitness and Sport-Specific Performance According to Maturity: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis.Sports Med Open. 2023 Apr 10;9(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s40798-023-00568-6. Sports Med Open. 2023. PMID: 37036542 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Plyometric Jump Training on the Reactive Strength Index in Healthy Individuals Across the Lifespan: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis.Sports Med. 2023 May;53(5):1029-1053. doi: 10.1007/s40279-023-01825-0. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 36906633 Free PMC article.
-
Plyometric Jump Training Effects on Maximal Strength in Soccer Players: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis of Randomized-Controlled Studies.Sports Med Open. 2024 May 10;10(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40798-024-00720-w. Sports Med Open. 2024. PMID: 38727944 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of plyometric jump training on physical fitness attributes in basketball players: A meta-analysis.J Sport Health Sci. 2022 Nov;11(6):656-670. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2020.12.005. Epub 2020 Dec 24. J Sport Health Sci. 2022. PMID: 33359798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plyometric jump training effects on the physical fitness of individual-sport athletes: a systematic review with meta-analysis.PeerJ. 2021 Mar 1;9:e11004. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11004. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33717707 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of core stability exercises on balance ability of children and adolescents with intellectual disabilities: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 19;19(12):e0314664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314664. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39700130 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training on Basketball Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Sports Sci Med. 2025 Mar 1;24(1):31-51. doi: 10.52082/jssm.2025.31. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Sports Sci Med. 2025. PMID: 40046212 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise interventions to improve bone mineral density in athletes participating in low-impact sports: a scoping review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Jan 20;26(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08316-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 39833826 Free PMC article.
-
Plyometric-Jump Training Effects on Physical Fitness and Sport-Specific Performance According to Maturity: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis.Sports Med Open. 2023 Apr 10;9(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s40798-023-00568-6. Sports Med Open. 2023. PMID: 37036542 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of plyometric training on skill and physical performance in healthy tennis players: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Physiol. 2022 Nov 24;13:1024418. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1024418. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36505069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United States National Library of Medicine N. Medical subject headings, MeSH. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/?term=water+sport. 2021. Date of acces: 1st Jan 2021.
-
- Dictionary OAA. Water sports. https://www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com/definition/american_english/w.... Access date: 5th Jan 2022.
-
- FINA. 2021. Available from http://www.fina.org. Accessed 1st Jan 2021.
-
- IOC. Access date: 1st Jan 2021. https://olympics.com/en/sports/. 2021;International Olympic Committee.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

