Comparing Early-Stage Breast Cancer Patients with Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis with and without Completion Axillary Lymph Node Dissection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36037108
- PMCID: PMC9741898
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.8.2561
Comparing Early-Stage Breast Cancer Patients with Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis with and without Completion Axillary Lymph Node Dissection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Currently, the standard method for staging and treatment of axillary lymph nodes for early-stage breast cancer is sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB), while axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) is used in cases with palpable axillary lymph nodes or positive SLNB cases. The aim of this review was to compare overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), and axillary recurrence in early-stage breast cancer patients underwent SLNB or SLNB and completion ALND.
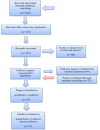
Methods: The databases of PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane Library were searched using the key words of "breast cancer", "axillary lymph node dissection", and "sentinel lymph node dissection". In addition, other sources were searched for ongoing studies (i.e., clinicaltrials.gov). The clinical trials were evaluated based on the Jadad quality criteria, and cohort studies were evaluated according to the STROBE criteria. At the end of the search, the articles were screened independently by two reviewers to check their eligibility to be included in the study. Afterwards, the data were extracted independently by two researchers.
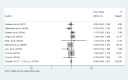
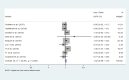
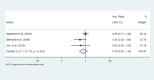
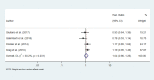
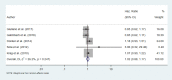
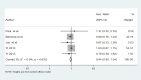
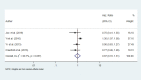
Results: After searching the databases, 169 papers were retrieved. However, after removing the duplicates and studying the titles and abstracts of these papers, only ten ones underwent further investigation. After reading full-text of each article, four studies were finalized. Following a manual search, 27 papers were entered into the study for the final evaluation, 11 of which were included in the meta-analysis based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The findings showed no significant differences in OS, DFS, and axillary recurrence in early-stage breast cancer patients underwent SLNB or SLNB and completion ALND.
Conclusion: The findings did not confirm that ALND improved OS, DFS, and axillary recurrence in patients who were clinically node-negative and positive SLNB.
Keywords: axillary lymph node dissection; early-stage breast cancer; sentinel lymph node biopsy; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety comparison between axillary lymph node dissection with no axillary surgery in patients with sentinel node-positive breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Surg. 2023 Jul 26;23(1):209. doi: 10.1186/s12893-023-02101-8. BMC Surg. 2023. PMID: 37495945 Free PMC article.
-
Axillary Lymph Node Dissection is Associated with Improved Survival Among Men with Invasive Breast Cancer and Sentinel Node Metastasis.Ann Surg Oncol. 2023 Sep;30(9):5610-5618. doi: 10.1245/s10434-023-13475-7. Epub 2023 May 19. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37204557
-
Effect of T Stages on the Choice of Axillary Evaluation Modality in Breast Cancer Patients With 1-2 Sentinel Lymph Node Metastases.Clin Breast Cancer. 2024 Jun;24(4):e232-e243.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2024.01.012. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Clin Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38368246
-
Long-term survival after sentinel lymph node biopsy or axillary lymph node dissection in pN0 breast cancer patients: a population-based study.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Dec;196(3):613-622. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06746-6. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 36207619
-
Axillary lymph node dissection vs. sentinel node biopsy for early-stage clinically node-negative breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022 Oct;306(4):1221-1234. doi: 10.1007/s00404-022-06458-8. Epub 2022 Mar 5. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022. PMID: 35249123
Cited by
-
Current axillary management of patients with early breast cancer and low-volume nodal disease undergoing primary surgery: results of a United Kingdom national practice survey.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Aug;206(3):465-471. doi: 10.1007/s10549-024-07328-4. Epub 2024 May 10. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38724821 Free PMC article.
-
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy vs. Axillary Lymph Node Dissection for Early-Stage Breast Cancer and Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis With Special Focus on Locoregional Recurrence and Regional Node Irradiation.Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2025 May 8;19:11782234251335409. doi: 10.1177/11782234251335409. eCollection 2025. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2025. PMID: 40351544 Free PMC article.
-
Consensus process to agree upon surgical quality assurance processes within a pragmatic, multicentre randomised clinical trial comparing targeted axillary dissection and axillary node clearance: the TADPOLE-TOGETHER project.BMJ Open. 2025 Jun 3;15(6):e095774. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-095774. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40461151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bansal M, Mohanti BK. Sentinel lymph node biopsy, axillary dissection and breast cancer: Radiation oncologist’s viewpoint. Nat Med J India. 2002;15:154–7. - PubMed
-
- Bilimoria KY, Bentrem DJ, Hansen NM, et al. Comparison of sentinel lymph node biopsy alone and completion axillary lymph node dissection for node-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2946–53. - PubMed
-
- Burak Jr WE, Hollenbeck ST, Zervos EE, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy results in less postoperative morbidity compared with axillary lymph node dissection for breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2002;183:23–7. - PubMed
-
- Canavese G, Bruzzi P, Catturich A, et al. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Versus Axillary Dissection in Node-Negative Early-Stage Breast Cancer: 15-Year Follow-Up Update of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23:2494–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

