Nucleation of the destruction complex on the centrosome accelerates degradation of β-catenin and regulates Wnt signal transmission
- PMID: 36037369
- PMCID: PMC9457612
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2204688119
Nucleation of the destruction complex on the centrosome accelerates degradation of β-catenin and regulates Wnt signal transmission
Abstract
Wnt signal transduction is controlled by the destruction complex (DC), a condensate comprising scaffold proteins and kinases that regulate β-catenin stability. Overexpressed DC scaffolds undergo liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS), but DC mesoscale organization at endogenous expression levels and its role in β-catenin processing were previously unknown. Here, we find that DC LLPS is nucleated by the centrosome. Through a combination of CRISPR-engineered custom fluorescent tags, finite element simulations, and optogenetic tools that allow for manipulation of DC concentration and multivalency, we find that centrosomal nucleation drives processing of β-catenin by colocalizing DC components to a single reaction crucible. Enriching GSK3β partitioning on the centrosome controls β-catenin processing and prevents Wnt-driven embryonic stem cell differentiation to mesoderm. Our findings demonstrate the role of nucleators in controlling biomolecular condensates and suggest tight integration between Wnt signal transduction and the cell cycle.
Keywords: LLPS; Wnt; destruction complex; optogenetics; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
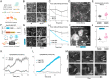


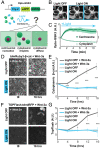

Comment in
-
To condense or not to condense: Wnt regulation by centrosome-nucleated biomolecular condensates.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 11;119(41):e2213905119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2213905119. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36179040 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The A-Kinase Anchoring Protein (AKAP) Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β Interaction Protein (GSKIP) Regulates β-Catenin through Its Interactions with Both Protein Kinase A (PKA) and GSK3β.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 9;291(37):19618-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.738047. Epub 2016 Aug 2. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27484798 Free PMC article.
-
Phase separation of Axin organizes the β-catenin destruction complex.J Cell Biol. 2021 Apr 5;220(4):e202012112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202012112. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33651074 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid-liquid phase separation drives the β-catenin destruction complex formation.Bioessays. 2021 Oct;43(10):e2100138. doi: 10.1002/bies.202100138. Epub 2021 Aug 21. Bioessays. 2021. PMID: 34418117
-
β-catenin at the centrosome: discrete pools of β-catenin communicate during mitosis and may co-ordinate centrosome functions and cell cycle progression.Bioessays. 2013 Sep;35(9):804-9. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300045. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Bioessays. 2013. PMID: 23804296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toggling a conformational switch in Wnt/β-catenin signaling: regulation of Axin phosphorylation. The phosphorylation state of Axin controls its scaffold function in two Wnt pathway protein complexes.Bioessays. 2013 Dec;35(12):1063-70. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300101. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Bioessays. 2013. PMID: 24105937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wnt target gene activation requires β-catenin separation into biomolecular condensates.PLoS Biol. 2024 Sep 24;22(9):e3002368. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002368. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39316611 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-resonance in developmental signaling regulates cell fate decisions.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 23:2025.02.04.636331. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.04.636331. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39990305 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the development and therapeutic resistance of non-small cell lung cancer.J Transl Med. 2024 Jun 13;22(1):565. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05380-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38872189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proofreading and single-molecule sensitivity in T cell receptor signaling by condensate nucleation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jun 3;122(22):e2422787122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2422787122. Epub 2025 May 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40445763
-
Wnt target IQGAP3 promotes Wnt signaling via disrupting Axin1-CK1α interaction.Oncogene. 2025 Aug 19. doi: 10.1038/s41388-025-03512-y. Online ahead of print. Oncogene. 2025. PMID: 40830657
References
-
- Kusserow A., et al. , Unexpected complexity of the Wnt gene family in a sea anemone. Nature 433, 156–160 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Nusse R., Clevers H., Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell 169, 985–999 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Clevers H., Wnt/β-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 127, 469–480 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Li V. S. W., et al. , Wnt signaling through inhibition of β-catenin degradation in an intact Axin1 complex. Cell 149, 1245–1256 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Cliffe A., Hamada F., Bienz M., A role of Dishevelled in relocating Axin to the plasma membrane during wingless signaling. Curr. Biol. 13, 960–966 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

