Nile waterscapes facilitated the construction of the Giza pyramids during the 3rd millennium BCE
- PMID: 36037388
- PMCID: PMC9477388
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2202530119
Nile waterscapes facilitated the construction of the Giza pyramids during the 3rd millennium BCE
Abstract
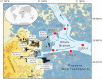
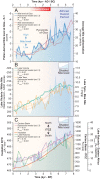
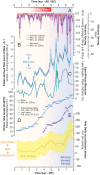
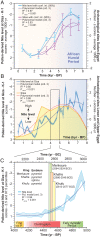
The pyramids of Giza originally overlooked a now defunct arm of the Nile. This fluvial channel, the Khufu branch, enabled navigation to the Pyramid Harbor complex but its precise environmental history is unclear. To fill this knowledge gap, we use pollen-derived vegetation patterns to reconstruct 8,000 y of fluvial variations on the Giza floodplain. After a high-stand level concomitant with the African Humid Period, our results show that Giza's waterscapes responded to a gradual insolation-driven aridification of East Africa, with the lowest Nile levels recorded at the end of the Dynastic Period. The Khufu branch remained at a high-water level (∼40% of its Holocene maximum) during the reigns of Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure, facilitating the transportation of construction materials to the Giza Pyramid Complex.
Keywords: Giza Harbour; Great pyramid; Nile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ancient Egyptian chronology and the astronomical orientation of pyramids.Nature. 2000 Nov 16;408(6810):320-4. doi: 10.1038/35042510. Nature. 2000. PMID: 11099032
-
Tracking Nile Delta vulnerability to Holocene change.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 29;8(7):e69195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069195. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23922692 Free PMC article.
-
Eyewitness introduction to Egypt: "The gift of the Nile".ABNF J. 2009 Fall;20(4):112-4. ABNF J. 2009. PMID: 19927898
-
Mysterious Civilizations: Is There a Connection between Medicine and Architecture in Ancient Egypt and Peru?Cureus. 2019 Apr 30;11(4):e4576. doi: 10.7759/cureus.4576. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31281759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology of Schistosomiasis in Egypt: Travel through Time: Review.J Adv Res. 2013 Sep;4(5):425-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2012.07.003. Epub 2012 Sep 4. J Adv Res. 2013. PMID: 25685449 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Konark Temple's Construction: A Critical Review of the Historical, Cultural, and Scientific Evidence.F1000Res. 2025 May 15;13:1540. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.157831.2. eCollection 2024. F1000Res. 2025. PMID: 40585880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lateral river erosion impacts the preservation of Neolithic enclosures in alluvial plains.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 2;13(1):16566. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43849-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37783939 Free PMC article.
-
Pyramid building and collapse.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Sep 13;119(37):e2212483119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2212483119. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36040866 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Williams M. A. J., The Nile Basin: Quaternary Geology, Geomorphology and Prehistoric Environments (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2019).
-
- Shaw I., Ed., The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt (Oxford University Press; ) 2000).
-
- Bell B., The oldest records of the Nile floods. Geogr. J. 136, 569–573 (1970).
-
- Hassan F. A., Historical Nile floods and their implications for climatic change. Science 212, 1142–1145 (1981). - PubMed
-
- Lehner M., On the waterfront: Canals and harbors in the time of Giza pyramid-building. Aearagram 15, 13–23 (2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

